Management of acute aortic dissection and thoracic aortic rupture
- PMID: 29507729
- PMCID: PMC5831732
- DOI: 10.1186/s40560-018-0287-7
Management of acute aortic dissection and thoracic aortic rupture
Abstract
Background: Both acute aortic dissection and ruptured aortic aneurysm are leading causes of death in cardiovascular disease. These life-threatening conditions have recently been categorized as acute aortic syndrome. This review describes the etiology, clinical presentation, and therapeutic options for acute aortic syndrome including acute aortic dissection and ruptured aortic aneurysm.
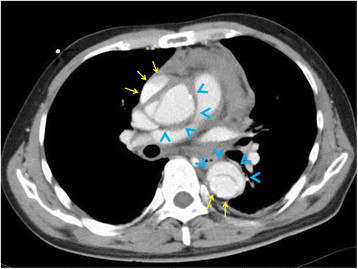
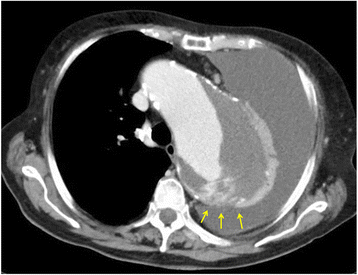
Main body: Several diagnostic tools for detecting these critical conditions have been developed including computed tomography, ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, and laboratory tests. Early and accurate diagnosis is most important to determine appropriate treatment. Initial treatment for these conditions should be aimed at controlling pain and the hemodynamic state with further treatment based on the imaging diagnosis and hematological assessment. Surgical outcomes after acute aortic syndrome are improving gradually; however, mortality remains high. Recently, thoracic endovascular aortic repair has become an alternative technique to treat complicated type B aortic dissection. Rapid treatment after early diagnosis is essential to save patients' lives.
Conclusions: Continuous advances in imaging and treatment technologies are improving short- and long-term outcomes in patients with acute aortic syndrome. Knowledge and interest in intensive care medicine in this area are contributing to improved outcomes, and further research into this life-threatening disease will lead to improvements in diagnosis and management.
Keywords: Acute aortic dissection; Acute aortic syndrome; Aortic aneurysm; Rupture; Stent graft.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Not applicable.The author declares that he has no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
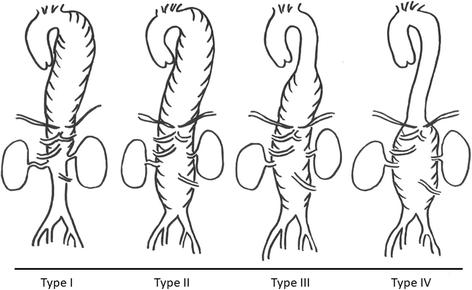
- Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, Bossone E, Bartolomeo RD, Eggebrecht H, Evangelista A, Falk V, Frank H, Gaemperli O, Grabenwöger M, Haverich A, Iung B, Manolis AJ, Meijboom F, Nienaber CA, Roffi M, Rousseau H, Sechtem U, Sirnes PA, Allmen RS, Vrints CJ, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2873–2926. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281. - DOI - PubMed
-
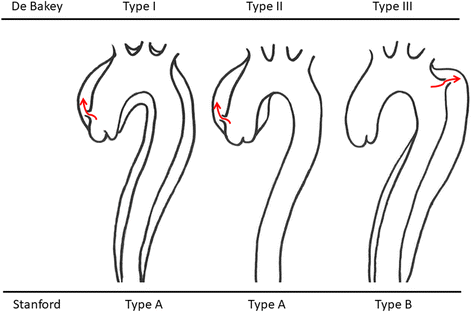
- DeBakey ME, Henly WS, Cooley DA, Morris GC, Jr, Crawford ES, Beall AC., Jr Surgical management of dissecting aneurysms of the aorta. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1965;49:130–149. - PubMed
-
- Hagan PG, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Bruckman D, Karavite DJ, Russman PL, Evangelista A, Fattori R, Suzuki T, Oh JK, Moore AG, Malouf JF, Pape LA, Gaca C, Sechtem U, Lenferink S, Deutsch HJ, Diedrichs H, Marcos y Robles J, Llovet A, Gilon D, Das SK, Armstrong WF, Deeb GM, Eagle KA. The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): new insights into an old disease. JAMA. 2000;283:897–903. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.7.897. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

