Long non-coding RNA MT1DP shunts the cellular defense to cytotoxicity through crosstalk with MT1H and RhoC in cadmium stress
- PMID: 29507753
- PMCID: PMC5824791
- DOI: 10.1038/s41421-017-0005-y
Long non-coding RNA MT1DP shunts the cellular defense to cytotoxicity through crosstalk with MT1H and RhoC in cadmium stress
Abstract
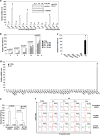
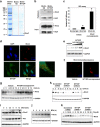
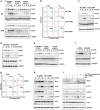
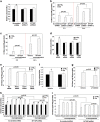
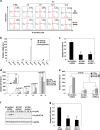
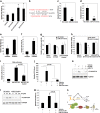
Metallothioneins (MTs) are known to protect cells against oxidative stress, especially providing protection against cadmium (Cd) toxicity in hepatocytes. There are various gene variants and pseudogenes for MTs; however, there is little understanding on the functions of those non-coding MT members that are known to be expressed as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) nowadays. Different from most protein-coding MT members, MT1DP was here found that remarkably induced to provoke cytotoxicity in hepatocytes in response to Cd treatment. MT1DP exerted such a pro-apoptotic function in Cd-treated hepatocytes through interacting with two partners: RhoC and MT1H. On one hand, MT1DP interacted with RhoC protein to increase the latter's stability by preventing lysosome-dependent protein degradation. Therefore, upon Cd stress, MT1DP/RhoC complex was quickly reinforced to activate RhoC-CCN1/2-AKT signaling and potentiate Ca2+ influx, leading to enhanced Cd uptake and elevated Cd toxicity. On the other hand, MT1H, a protein-coding member of the MT family with little known function, was found to quickly respond to Cd exposure along with MT1DP. Mechanistically, MT1H and MT1DP were uncovered to mutually protect each other through a reciprocal ceRNA mechanism, building up a positive feedback loop to enforce MT1DP-conducted signaling upon Cd exposure. Moreover, MT1DP was found to contribute much more to the activation of RhoC-CCN1/2-AKT signaling than MT1H. Considered together, we here unveiled a mystery whether a pseudogene within the MT family, MT1DP, has actual biological functions in regulating Cd-induced cellular defense. Our findings unearthed an important role of pseudogene MT1DP in calibrating the cellular machinery to switch the cellular defense to cytotoxicity through crosslinking an interplay between its two partners, namely MT1H and RhoC, under cadmium stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA MT1DP Aggravates Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress by Repressing the Function of Nrf2 and is Dependent on Interaction with miR-365.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018 Apr 24;5(7):1800087. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800087. eCollection 2018 Jul. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018. PMID: 30027041 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-derived exosome-laden lncRNA MT1DP aggravates cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity.Environ Pollut. 2020 Mar;258:113717. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113717. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Environ Pollut. 2020. PMID: 31864927
-
LncRNA MT1DP promotes cadmium-induced DNA replication stress by inhibiting chromatin recruitment of SMARCAL1.Sci Total Environ. 2022 Feb 10;807(Pt 3):151078. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151078. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 34715232
-
Role of metallothionein in cadmium traffic and toxicity in kidneys and other mammalian organs.Biometals. 2010 Oct;23(5):897-926. doi: 10.1007/s10534-010-9351-z. Epub 2010 Jun 15. Biometals. 2010. PMID: 20549307 Review.
-
Metallothionein transgenic and knock-out mouse models in the study of cadmium toxicity.J Toxicol Sci. 1998 Jul;23 Suppl 2:97-102. doi: 10.2131/jts.23.supplementii_97. J Toxicol Sci. 1998. PMID: 9760441 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Nrf2 signaling pathway in heart failure: Role of extracellular vesicles and non-coding RNAs.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 May 1;167:218-231. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.013. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33741451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA MT1DP Aggravates Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress by Repressing the Function of Nrf2 and is Dependent on Interaction with miR-365.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018 Apr 24;5(7):1800087. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800087. eCollection 2018 Jul. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018. PMID: 30027041 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicine initiates ferroptosis for enhanced lung cancer therapy.Drug Deliv. 2025 Dec;32(1):2527752. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2025.2527752. Epub 2025 Jul 5. Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40616599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemotherapy-initiated cysteine-rich protein 61 decreases acute B-lymphoblastic leukemia chemosensitivity.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Mar 26;150(3):159. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05692-8. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38530432 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal Osteoclast-Derived miRNA in Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Their Pathogenesis in Bone Erosion to New Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 25;25(3):1506. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031506. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

