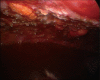
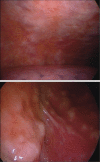
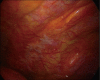
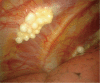
Endoscopic diagnosis and management of pleural effusion in malignant pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 29507795
- PMCID: PMC5830554
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.09.142
Endoscopic diagnosis and management of pleural effusion in malignant pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
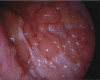
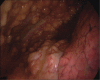
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an asbestos-related aggressive tumor, that requires proper diagnosis and management. Symptoms are nonspecific and chest computed tomography (CT) and chest ultrasound (US) are important radiological tools in the initial workup to identify early pathological signs. Performing a medical thoracoscopy (MT) is essential for a definitive diagnosis of MPM. The procedure, integrated with a prior US, allows a global evaluation of the pleural cavity and the execution of multiple targeted biopsies, with low risk of complications. Some different endoscopic patterns are recognized. Thoracoscopic biopsies provide enough material to allow a thorough pathological and immunohistochemical characterization. The presence of extensive pleural adhesions and critical patient conditions are the only absolute contraindications. The clinical course of MPM is characterized by chronic symptoms such as chest pain and progressive dyspnea, the latter caused mainly by recurrent pleural effusion. Palliative interventions are required in order to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life (QoL). These include thoracentesis, pleurodesis and the placement of an indwelling pleural catheter.
Keywords: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM); medical thoracoscopy (MT); pleural effusion; pleurodesis; thoracic ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Value of thoracoscopy and talc pleurodesis in diagnosis and palliative treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma].Praxis (Bern 1994). 1998 Mar 4;87(10):336-40. Praxis (Bern 1994). 1998. PMID: 9545840 Review. German.
-
A Case of Pulmonary Embolism with Sarcomatoid Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma with Long-Term Pleural Effusion.Onco Targets Ther. 2021 Jul 16;14:4231-4237. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S315869. eCollection 2021. Onco Targets Ther. 2021. PMID: 34295165 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Thoracoscopy, Computed Tomography-guided Biopsy, and Ultrasound-guided Biopsy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Systematic Review.Anticancer Res. 2021 May;41(5):2217-2225. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.14998. Anticancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33952448
-
Success rate of medical thoracoscopy and talc pleurodesis in malignant pleurisy: A single-centre experience.Respirology. 2018 Jun;23(6):613-617. doi: 10.1111/resp.13252. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Respirology. 2018. PMID: 29320805
-
A Rare Case of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma in a Young Healthy Male Without Asbestos Exposure.Cureus. 2021 Aug 15;13(8):e17199. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17199. eCollection 2021 Aug. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34540427 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Insights into Pleural Mesothelioma: Unveiling Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 24;15(11):1323. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111323. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40506895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Feasibility Pilot Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 26;16(11):2023. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112023. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893142 Free PMC article.
-
Rehabilitation for Functioning and Quality of Life in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: A Scoping Review.Curr Oncol. 2024 Jul 30;31(8):4318-4337. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31080322. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39195305 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of tuberculosis pleurisy with three endoscopic features via pleuroscopy.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021 Jan-Dec;15:1753466621989532. doi: 10.1177/1753466621989532. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021. PMID: 33541248 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources