DPP-4 Inhibitors as Treatments for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 29507862
- PMCID: PMC5817360
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/5308582
DPP-4 Inhibitors as Treatments for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: Several clinical studies have reported the application of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors as treatments for type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). This study aims to review the outcomes of these existing studies and to discuss the therapeutic effects of DPP-4 inhibitors on T1DM.
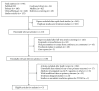
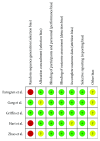
Methods: We thoroughly searched the Medline, Embase, PubMed, and Cochrane Library databases and ClinicalTrials.gov for studies concerning the use of DPP-4 inhibitors in patients with T1DM.
Results: In preclinical trials, DPP-4 inhibitors improved the pathogenesis of T1DM. However, only a portion of the studies showed potential efficacy regarding clinical glycemic control and other clinical parameters. From this meta-analysis, pooled data from 5 randomized controlled trials revealed that the additional use of DPP-4 inhibitors resulted in a greater decrease in glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels (0.07%, 95% CI (-0.37%-0.23%)) than insulin monotherapy, although the decrease was not significant. A small decrease in postprandial glucose or insulin consumption was confirmed.
Conclusion: Although DPP-4 inhibitors may be beneficial for T1DM, existing studies do not strongly support these positive effects in clinical practice. Further optimized clinical trials are needed.
Figures
References
-
- Gong C., Meng X., Jiang Y., Wang X., Cui H., Chen X. Trends in childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus incidence in Beijing from 1995 to 2010: a retrospective multicenter study based on hospitalization data. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics. 2015;17(3):159–165. doi: 10.1089/dia.2014.0205. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous