Treatment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies
- PMID: 29508455
- PMCID: PMC5844369
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.27344
Treatment of autonomic dysfunction in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies
Abstract
Dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system afflicts most patients with Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies such as dementia with Lewy bodies, multiple system atrophy, and pure autonomic failure, reducing quality of life and increasing mortality. For example, gastrointestinal dysfunction can lead to impaired drug pharmacodynamics causing a worsening in motor symptoms, and neurogenic orthostatic hypotension can cause syncope, falls, and fractures. When recognized, autonomic problems can be treated, sometimes successfully. Discontinuation of potentially causative/aggravating drugs, patient education, and nonpharmacological approaches are useful and should be tried first. Pathophysiology-based pharmacological treatments that have shown efficacy in controlled trials of patients with synucleinopathies have been approved in many countries and are key to an effective management. Here, we review the treatment of autonomic dysfunction in patients with Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies, summarize the nonpharmacological and current pharmacological therapeutic strategies including recently approved drugs, and provide practical advice and management algorithms for clinicians, with focus on neurogenic orthostatic hypotension, supine hypertension, dysphagia, sialorrhea, gastroparesis, constipation, neurogenic overactive bladder, underactive bladder, and sexual dysfunction. © 2018 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; autonomic failure; dysautonomia; multiple system atrophy; nonmotor symptoms; treatment.
© 2018 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures


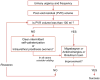
References
-
- Peelaerts W, Bousset L, Van der Perren A, et al. alpha-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature. 2015;522(7556):340–344. - PubMed
-
- Peelaerts W, Baekelandt V. a-Synuclein strains and the variable pathologies of synucleinopathies. Journal of neurochemistry. 2016;139(1):256–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

