Whole-Genome Sequencing of Pharmacogenetic Drug Response in Racially Diverse Children with Asthma
- PMID: 29509491
- PMCID: PMC6006403
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2529OC
Whole-Genome Sequencing of Pharmacogenetic Drug Response in Racially Diverse Children with Asthma
Abstract
Rationale: Albuterol, a bronchodilator medication, is the first-line therapy for asthma worldwide. There are significant racial/ethnic differences in albuterol drug response.
Objectives: To identify genetic variants important for bronchodilator drug response (BDR) in racially diverse children.
Methods: We performed the first whole-genome sequencing pharmacogenetics study from 1,441 children with asthma from the tails of the BDR distribution to identify genetic association with BDR.
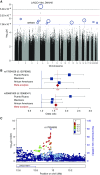
Measurements and main results: We identified population-specific and shared genetic variants associated with BDR, including genome-wide significant (P < 3.53 × 10-7) and suggestive (P < 7.06 × 10-6) loci near genes previously associated with lung capacity (DNAH5), immunity (NFKB1 and PLCB1), and β-adrenergic signaling (ADAMTS3 and COX18). Functional analyses of the BDR-associated SNP in NFKB1 revealed potential regulatory function in bronchial smooth muscle cells. The SNP is also an expression quantitative trait locus for a neighboring gene, SLC39A8. The lack of other asthma study populations with BDR and whole-genome sequencing data on minority children makes it impossible to perform replication of our rare variant associations. Minority underrepresentation also poses significant challenges to identify age-matched and population-matched cohorts of sufficient sample size for replication of our common variant findings.
Conclusions: The lack of minority data, despite a collaboration of eight universities and 13 individual laboratories, highlights the urgent need for a dedicated national effort to prioritize diversity in research. Our study expands the understanding of pharmacogenetic analyses in racially/ethnically diverse populations and advances the foundation for precision medicine in at-risk and understudied minority populations.
Keywords: Latinos; NFKB1; albuterol; asthma; minority.
Figures

Comment in
-
Assessing Asthma Medication Responses in U.S. Minority Children by Whole-Genome Sequencing.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Jun 15;197(12):1513-1514. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201803-0457ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29578752 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Asthma. 2017 [accessed 2017 Sep 12]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs307/en/
-
- Akinbami L. Asthma prevalence, health care use and mortality: United States, 2003-05. 2015 [accessed 2017 Sep 12]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hestat/asthma03-05/asthma03-05.htm. - PubMed
-
- Palmer LJ, Silverman ES, Weiss ST, Drazen JM. Pharmacogenetics of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:861–866. - PubMed
-
- Eggleston PA, Malveaux FJ, Butz AM, Huss K, Thompson L, Kolodner K, et al. Medications used by children with asthma living in the inner city. Pediatrics. 1998;101:349–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 ES015794/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL130629/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK113003/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA197139/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008901/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL066289/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES024844/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118267/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL125666/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 HL140218/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12 GM081266/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079139/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG008684/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD085993/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133433/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES013508/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 MD006902/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL135403/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K25 HL121295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138424/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD010443/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- RL5 GM118984/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL132821/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

