The Role of mTOR in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Future Cornerstone of a Winning Strategy?
- PMID: 29509701
- PMCID: PMC5877608
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030747
The Role of mTOR in Neuroendocrine Tumors: Future Cornerstone of a Winning Strategy?
Abstract
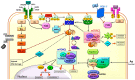
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) is part of the phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AkT)/mTOR pathway and owes its name to the inhibitory effect of rapamycin. The mTOR has a central converging role for many cell functions, serving as a sensor for extracellular signals from energy status and nutrients availability, growth factors, oxygen and stress. Thus, it also modulates switch to anabolic processes (protein and lipid synthesis) and autophagy, in order to regulate cell growth and proliferation. Given its functions in the cell, its deregulation is implicated in many human diseases, including cancer. Its predominant role in tumorigenesis and progression of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), in particular, has been demonstrated in preclinical studies and late clinical trials. mTOR inhibition by everolimus is an established therapeutic target in NETs, but there are no identified predictive or prognostic factors. This review is focused on the role of mTOR and everolimus in NETs, from preclinical studies to major clinical trials, and future perspectives involving mTOR in the treatment of NETs.
Keywords: Akt; PTEN; RAD001; RADIANT; carcinoid; everolimus; mTOR; mTORC1; neuroendocrine tumor; neuroendocrine tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yao J.C., Hassan M., Phan A., Dagohoy C., Leary C., Mares J.E., Abdalla E.K., Fleming J.B., Vauthey J.-N., Rashid A., et al. One hundred years after “carcinoid”: Epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:3063–3072. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.4377. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

