Effects of Cholesterol Levels on Mortality in Patients with Long-Term Peritoneal Dialysis Based on Residual Renal Function
- PMID: 29510483
- PMCID: PMC5872718
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10030300
Effects of Cholesterol Levels on Mortality in Patients with Long-Term Peritoneal Dialysis Based on Residual Renal Function
Abstract
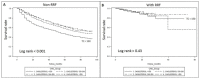
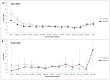
The effect of dyslipidemia on peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients based on the presence of residual renal function (RRF; renal creatinine clearance >2 mL/min/1.73 m²) is unknown. Data from the Taiwan Renal Registry Data System between 2005 and 2012 were analyzed to estimate the association between dyslipidemia and mortality in PD patients. Long-term PD patients (n = 8032) were divided into groups with (RRF; n = 2691, 33.5%) and without RRF (non-RRF; n = 5341, 66.5%). The primary outcome was three-year mortality, and multivariate Cox regression was used for survival analysis. After stratifying the total cholesterol (TC) level between the first and third years, the hazard ratio for mortality was estimated. In the non-RRF group, TC < 120 mg/dL was associated with independently increased risk of mortality. In the RRF group, low TC was not independently correlated with increased mortality, but TC > 285 mg/dL was associated with increased risk. PD patients with higher level of TC (>200 mg/dL) in both first and third years of dialysis had significantly lower risk of mortality. In this nationwide cohort study, PD patients without RRF who had low TC level had the highest mortality, in contrast to those with RRF. Malnutrition in long-term PD patients without RRF is an important issue to be monitored.
Keywords: lipid; malnutrition; mortality; peritoneal dialysis; residual renal function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular volume expansion and the preservation of residual renal function in Korean peritoneal dialysis patients: a long-term follow up study.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016 Oct;20(5):778-786. doi: 10.1007/s10157-015-1203-2. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26611535
-
Association between residual renal function, inflammation and patient survival in new peritoneal dialysis patients.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003 Mar;18(3):590-7. doi: 10.1093/ndt/18.3.590. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003. PMID: 12584284
-
Rate of decline of residual renal function is associated with all-cause mortality and technique failure in patients on long-term peritoneal dialysis.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009 Sep;24(9):2909-14. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp056. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19225016
-
Effect of neutral pH and low-glucose degradation product-containing peritoneal dialysis solution on residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis patients: a meta-analysis.Nephron. 2015;129(3):155-63. doi: 10.1159/000368235. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Nephron. 2015. PMID: 25765060 Review.
-
[Factors related to loss of residual renal function in peritoneal dialysis].Nefrologia. 2008;28 Suppl 6:39-44. Nefrologia. 2008. PMID: 18957011 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Total cholesterol and mortality in peritoneal dialysis: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2023 May 23;24(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03187-1. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37221481 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Dyslipidemia and Peritoneal Dialysis Technique Survival.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019 Jul 25;7(15):2467-2473. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.664. eCollection 2019 Aug 15. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31666849 Free PMC article.
-
Serum alkaline phosphatase levels correlate with long-term mortality solely in peritoneal dialysis patients with residual renal function.Ren Fail. 2019 Nov;41(1):718-725. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1646662. Ren Fail. 2019. PMID: 31409217 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant serum parathyroid hormone, calcium, and phosphorus as risk factors for peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80938-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441921 Free PMC article.
-
Dyslipidemia in Peritoneal Dialysis: Implications for Peritoneal Membrane Function and Patient Outcomes.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 17;12(10):2377. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102377. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shoji T., Abe T., Matsuo H., Egusa G., Yamasaki Y., Kashihara N., Shirai K., Kashiwagi A., Committee of Renal and Peripheral Arteries. Japan Atherosclerosis Society Chronic kidney disease, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2012;19:299–315. doi: 10.5551/jat.10454. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Samouilidou E.C., Karpouza A.P., Kostopoulos V., Bakirtzi T., Pantelias K., Petras D., Tzanatou-Exarchou H.J., Grapsa E. Lipid abnormalities and oxidized LDL in chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Ren. Fail. 2012;34:160–164. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2011.641515. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

