TIPE3 differentially modulates proliferation and migration of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells via distinct subcellular location
- PMID: 29510688
- PMCID: PMC5840720
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4177-0
TIPE3 differentially modulates proliferation and migration of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells via distinct subcellular location
Abstract
Background: TIPE3 (TNFAIP8L3), a transfer protein for lipid second messengers, is upregulated in human lung cancer tissues. The most popular lung cancer is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with high incidences and low survival rates, while the roles of TIPE3 in NSCLC remain largely unknown.
Methods: TIPE3 expression was examined in tissue chips from patients with NSCLC using immunohistochemistry; the correlation of plasma membrane expression of TIPE3 with T stage of NSCLC was analyzed. After endogenous TIPE3 was silenced via siRNA, or TIPE3 with N or C-terminal flag was overexpressed via transient or stable transfection, human NSCLC cells were assayed for the proliferation and migration, respectively. NSCLC cells, in which TIPE3 with C-terminal flag was stably transfected, were inoculated into mice to establish xenograft tumors, the tumor growth and the expression of TIPE3 in tumor tissues were examined.
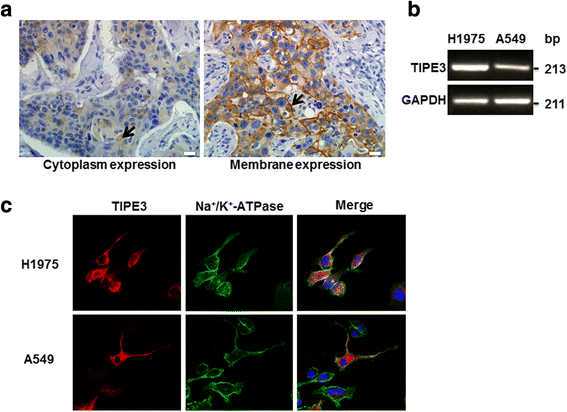
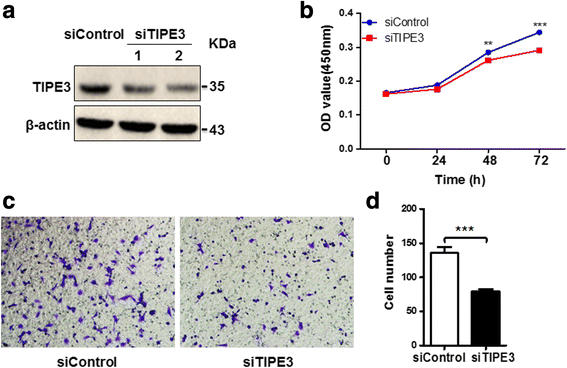
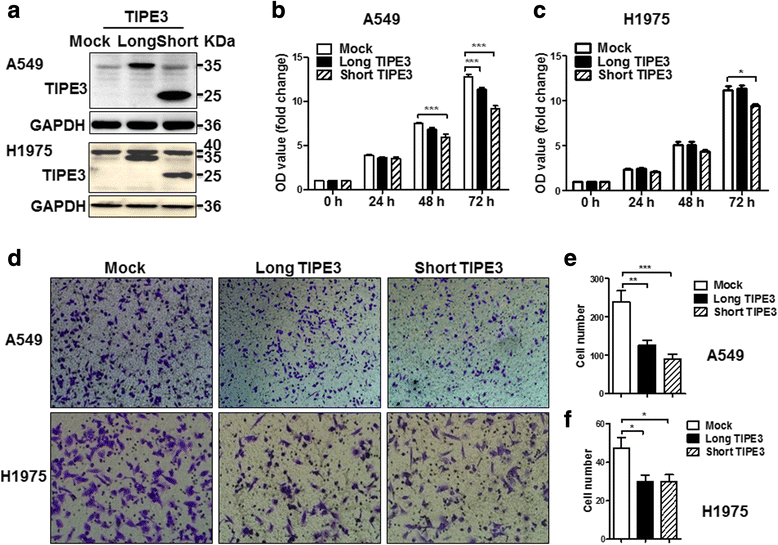
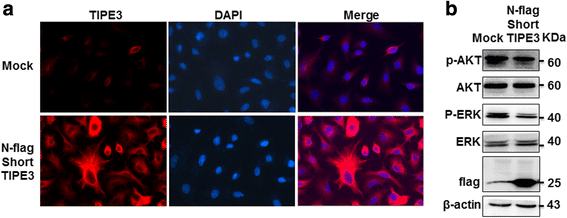
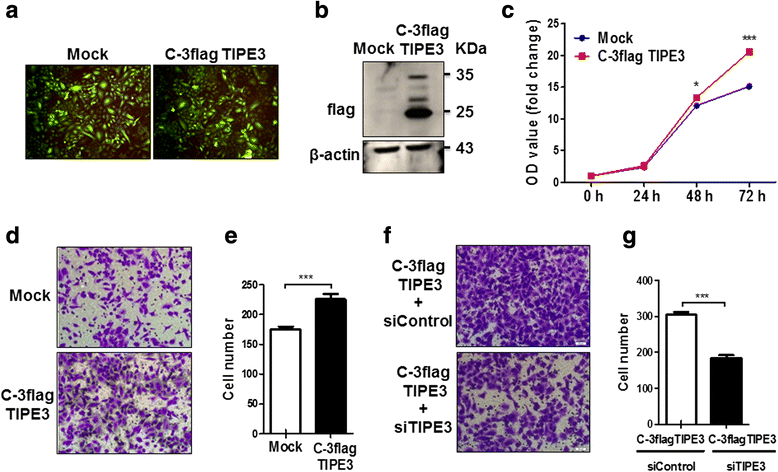
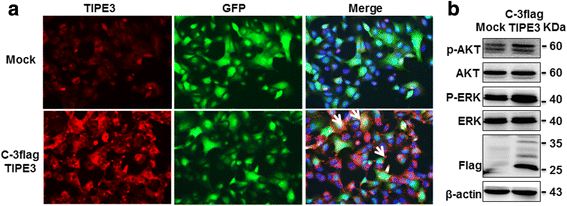
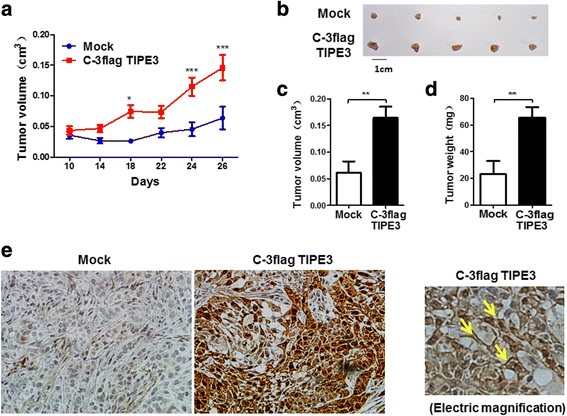
Results: TIPE3 was broadly expressed in lung tissues of patients with NSCLC. The plasma membrane expression of TIPE3 was positively correlated with the T stage of NSCLC. Knockdown of endogenous TIPE3, which was predominantly expressed in the plasma membrane, inhibited the proliferation and migration of NSCLC cells. While transient overexpression of TIPE3 with N-terminal flag, which was mostly trapped in the cytoplasm, inhibited the growth and migration of NSCLC cells accompanied by inactivation of AKT and ERK. In contrast, stable overexpression of TIPE3 with C-terminal flag, which could be localized in the plasma membrane, markedly promoted the growth and migration of NSCLC cells through activation of AKT and ERK. Notably, in xenograft tumor models established with NSCLC cells, stable overexpression of TIPE3 with C-terminal flag in NSCLC cells significantly promoted the tumor growth and enhanced the expression and plasma membrane localization of TIPE3 in tumor tissues.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that human TIPE3 promotes the proliferation and migration of NSCLC cells depending on its localization on plasma membrane, whereas cytoplasmic TIPE3 may exert a negative function. Thus, manipulating the subcellular location of TIPE3 can be a promising strategy for NSCLC therapy.
Keywords: Migration; Non-small-cell lung cancer; Proliferation; TIPE3.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All human and animal study protocols were approved by Ethical Review Board of Shandong University. For study on human tissue arrays obtained from Outdo Biotech Co., Shanghai, China, informed consent has been waived by Ethical Review Board of Shandong University. All animal-related procedures were in accordance with the institutional guidelines for animal care and utilization.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TIPE Family of Proteins and Its Implications in Different Chronic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 29;19(10):2974. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102974. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30274259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TIPE3 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via the protein kinase B/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-glycogen synthase kinase 3β-β-catenin/Snail axis.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;10(2):936-954. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-147. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33718034 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulated expression of TIPE3 inhibits malignant progression of non-small cell lung cancer via Wnt signaling.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Jun 15;439(2):114093. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114093. Epub 2024 May 15. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38759744
-
TIPE3 protein promotes breast cancer metastasis through activating AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 25;8(30):48889-48904. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16522. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28388580 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-92a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer metastasis.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jul;51(1):235-244. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3999. Epub 2017 May 16. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28534966
Cited by
-
TIPE1 Suppresses Growth and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer.J Oncol. 2021 Jun 3;2021:5538911. doi: 10.1155/2021/5538911. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34188681 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α-inducible protein 8-like protein 3 (TIPE3): a novel prognostic factor in colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2023 Feb 8;23(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10590-2. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36755222 Free PMC article.
-
TIPE Family of Proteins and Its Implications in Different Chronic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 29;19(10):2974. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102974. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30274259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TIPE3 promotes drug resistance in colorectal cancer by enhancing autophagy via the USP19/Beclin1 pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Apr 25;11(1):202. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02477-x. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40280943 Free PMC article.
-
TIPE3 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via the protein kinase B/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-glycogen synthase kinase 3β-β-catenin/Snail axis.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;10(2):936-954. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-147. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33718034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Howington JA, Blum MG, Chang AC, Balekian AA, Murthy SC. Treatment of stage I and II non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e278S–e313S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2359. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ramnath N, Dilling TJ, Harris LJ, et al. Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e314S–e340S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2360. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Evans T, Gettinger S, et al. Treatment of stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e341S–e368S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2361. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81471065/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81770838/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 31470856/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 91439124/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81101982/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

