Adapting the Wii Fit Balance Board to Enable Active Video Game Play by Wheelchair Users: User-Centered Design and Usability Evaluation
- PMID: 29510972
- PMCID: PMC5861301
- DOI: 10.2196/rehab.8003
Adapting the Wii Fit Balance Board to Enable Active Video Game Play by Wheelchair Users: User-Centered Design and Usability Evaluation
Abstract
Background: Active video game (AVG) playing, also known as "exergaming," is increasingly employed to promote physical activity across all age groups. The Wii Fit Balance Board is a popular gaming controller for AVGs and is used in a variety of settings. However, the commercial off-the-shelf (OTS) design poses several limitations. It is inaccessible to wheelchair users, does not support the use of stabilization assistive devices, and requires the ability to shift the center of balance (COB) in all directions to fully engage in game play.
Objective: The aim of this study was to design an adapted version of the Wii Fit Balance Board to overcome the identified limitations and to evaluate the usability of the newly designed adapted Wii Fit Balance Board in persons with mobility impairments.
Methods: In a previous study, 16 participants tried the OTS version of the Wii Fit Balance Board. On the basis of observed limitations, a team of engineers developed and adapted the design of the Wii Fit Balance Board, which was then subjected to multiple iterations of user feedback and design tweaks. On design completion, we recruited a new pool of participants with mobility impairments for a larger study. During their first visit, we assessed lower-extremity function using selected mobility tasks from the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health. During a subsequent session, participants played 2 sets of games on both the OTS and adapted versions of the Wii Fit Balance Board. Order of controller version played first was randomized. After participants played each version, we administered the System Usability Scale (SUS) to examine the participants' perceived usability.
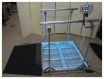
Results: The adapted version of the Wii Fit Balance Board resulting from the user-centered design approach met the needs of a variety of users. The adapted controller (1) allowed manual wheelchair users to engage in game play, which was previously not possible; (2) included Americans with Disabilities Act-compliant handrails as part of the controller, enabling stable and safe game play; and (3) included a sensitivity control feature, allowing users to fine-tune the controller to match the users' range of COB motion. More than half the sample could not use the OTS version of the Wii Fit Balance Board, while all participants were able to use the adapted version. All participants rated the adapted Wii Fit Balance Board at a minimum as "good," while those who could not use the OTS Wii Fit Balance Board rated the adapted Wii Fit Balance Board as "excellent." We found a significant negative correlation between lower-extremity function and differences between OTS and adapted SUS scores, indicating that as lower-extremity function decreased, participants perceived the adapted Wii Fit Balance Board as more usable.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated a successful adaptation of a widely used AVG controller. The adapted controller's potential to increase physical activity levels among people with mobility impairments will be evaluated in a subsequent trial.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02994199; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02994199 (Archived by WebCite at http://www.webcitation.org/6xWTyiJWf).
Keywords: Wii Fit; active video gaming; equipment design; exercise; physical activity; physical disability; rehabilitation; sedentary lifestyle; usability; video games; wheelchairs.
©Mohanraj Thirumalai, William B Kirkland, Samuel R Misko, Sangeetha Padalabalanarayanan, Laurie A Malone. Originally published in JMIR Rehabilitation and Assistive Technology (http://rehab.jmir.org), 06.03.2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Active Video Gaming Using an Adapted Gaming Mat in Youth and Adults With Physical Disabilities: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2021 Aug 26;9(3):e30672. doi: 10.2196/30672. JMIR Serious Games. 2021. PMID: 34435962 Free PMC article.
-
Energy Expenditure and Enjoyment During Active Video Gaming Using an Adapted Wii Fit Balance Board in Adults with Physical Disabilities: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2019 Feb 1;7(1):e11326. doi: 10.2196/11326. JMIR Serious Games. 2019. PMID: 30707098 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Active Video Gaming Using Adapted Controllers by Individuals With Physical Disabilities: A Protocol.JMIR Res Protoc. 2017 Jun 16;6(6):e116. doi: 10.2196/resprot.7621. JMIR Res Protoc. 2017. PMID: 28623186 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Wii Fit Exercise With Balance and Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 6;9:812570. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.812570. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35602499 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Synthesis of Nintendo Wii Fit Gaming Protocol in Addressing Balance Among Healthy Older Adults: What System Works?Games Health J. 2017 Apr;6(2):65-74. doi: 10.1089/g4h.2016.0082. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Games Health J. 2017. PMID: 28225644 Review.
Cited by
-
The Usability of a Touchpad Active Video Game Controller for Individuals With Impaired Mobility: Observational Study.JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2023 Aug 3;10:e41993. doi: 10.2196/41993. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol. 2023. PMID: 37535411 Free PMC article.
-
Active Video Gaming Using an Adapted Gaming Mat in Youth and Adults With Physical Disabilities: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2021 Aug 26;9(3):e30672. doi: 10.2196/30672. JMIR Serious Games. 2021. PMID: 34435962 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Wii Fit-based Exercises versus proprioceptive training on balance and fall risk in patients with diabetic neuropathy.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Feb;41(2):393-398. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.2.8775. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39926688 Free PMC article.
-
Usability of the GAIMplank Video Game Controller for People With Mobility Impairments: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2023 Jan 10;11:e38484. doi: 10.2196/38484. JMIR Serious Games. 2023. PMID: 36626195 Free PMC article.
-
Energy Expenditure and Enjoyment During Active Video Gaming Using an Adapted Wii Fit Balance Board in Adults with Physical Disabilities: Observational Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2019 Feb 1;7(1):e11326. doi: 10.2196/11326. JMIR Serious Games. 2019. PMID: 30707098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnett A, Cerin E, Baranowski T. Active video games for youth: a systematic review. J Phys Act Health. 2011 Jul;8(5):724–37. - PubMed
-
- LeBlanc AG, Chaput J, McFarlane A, Colley RC, Thivel D, Biddle SJH, Maddison R, Leatherdale ST, Tremblay MS. Active video games and health indicators in children and youth: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e65351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065351. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0065351 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

