Suitability of the simplified autoimmune hepatitis score for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis in a German cohort
- PMID: 29511554
- PMCID: PMC5833219
- DOI: 10.1177/2050640617711632
Suitability of the simplified autoimmune hepatitis score for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis in a German cohort
Abstract
Background: Several years ago the International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group simplified the previous revised original scoring system for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) into a scoring system based on only four instead of 13 parameters.
Objective: We aimed to evaluate the suitability of the simplified AIH score for diagnosis of AIH in a German cohort with chronic liver diseases.
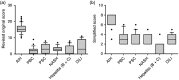
Methods: In this retrospective single-center study, we compared the accuracy of both AIH scores in 70 patients with AIH and 211 patients with chronic liver diseases (PBC (n = 52), PSC (n = 27), NASH (n = 67), DILI (n = 15), CHB/C (n = 50)). Sensitivity, specificity and predictability of each scoring system were calculated.
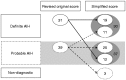
Results: Using the simplified AIH score, the sensitivity and specificity of detecting a probable AIH (scores ≥ 6) were 96% and 97% with a positive and negative predictive value of 92% and 99%, respectively. For diagnosis of definite AIH (scores ≥ 7), the sensitivity and specificity were 43% and 100% with a positive and negative predictive value of 97% and 84%, respectively. The concordance with the revised original criteria was 63%. The specificity for excluding AIH was excellent in both scoring system.
Conclusion: The simplified diagnostic criteria allow a reliable diagnosis of AIH in a German cohort.
Keywords: Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH); diagnostic scores; revised original criteria; routine clinical practice; simplified criteria.
Figures
References
-
- Czaja AJ, Ammon HV, Summerskill WH. Clinical features and prognosis of severe chronic active liver disease (CALD) after corticosteroid-induced remission. Gastroenterology 1980; 78: 518–523. - PubMed
-
- Krawitt EL. Autoimmune hepatitis. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 54–66. - PubMed
-
- Manns MP, Czaja AJ, Gorham JD, et al. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2010; 51: 2193–2213. - PubMed
-
- Kogan J, Safadi R, Ashur Y, et al. Prognosis of symptomatic versus asymptomatic autoimmune hepatitis: A study of 68 patients. J Clin Gastroenterol 2002; 35: 75–81. - PubMed
-
- Kessler WR, Cummings OW, Eckert G, et al. Fulminant hepatic failure as the initial presentation of acute autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 2: 625–631. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources