The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug
- PMID: 29511601
- PMCID: PMC5835698
The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug
Abstract
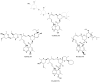
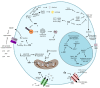
Drug repositioning is a highly studied alternative strategy to discover and develop anticancer drugs. This drug development approach identifies new indications for existing compounds. Ivermectin belongs to the group of avermectins (AVM), a series of 16-membered macrocyclic lactone compounds discovered in 1967, and FDA-approved for human use in 1987. It has been used by millions of people around the world exhibiting a wide margin of clinical safety. In this review, we summarize the in vitro and in vivo evidences demonstrating that ivermectin exerts antitumor effects in different types of cancer. Ivermectin interacts with several targets including the multidrug resistance protein (MDR), the Akt/mTOR and WNT-TCF pathways, the purinergic receptors, PAK-1 protein, certain cancer-related epigenetic deregulators such as SIN3A and SIN3B, RNA helicase, chloride channel receptors and preferentially target cancer stem-cell like population. Importantly, the in vitro and in vivo antitumor activities of ivermectin are achieved at concentrations that can be clinically reachable based on the human pharmacokinetic studies done in healthy and parasited patients. Thus, existing information on ivermectin could allow its rapid move into clinical trials for cancer patients.
Keywords: Ivermectin; cancer; drug repurposing.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Crump A. Ivermectin: enigmatic multifaceted ‘wonder’ drug continues to surprise and exceed expectations. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2017;70:495–505. - PubMed
-
- Bai SH, Ogbourne S. Eco-toxicological effects of the avermectin family with a focus on abamectin and ivermectin. Chemosphere. 2016;154:204–214. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Luo M, Xu W, Yang M, Wang B, Gao J, Li Y, Tao L. Avermectin confers its cytotoxic effects by inducing DNA damage and mitochondria-associated apoptosis. J Agric Food Chem. 2016;64:6895–902. - PubMed
-
- Alberich M, Ménez C, Sutra JF, Lespine A. Ivermectin exposure leads to up-regulation of detoxification genes in vitro and in vivo in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;740:428–35. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
