Prostate cancer in Asia: A collaborative report
- PMID: 29511634
- PMCID: PMC5832886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajur.2014.08.007
Prostate cancer in Asia: A collaborative report
Abstract
The incidence of prostate cancer (PCa) within Asian population used to be much lower than in the Western population; however, in recent years the incidence and mortality rate of PCa in some Asian countries have grown rapidly. This collaborative report summarized the latest epidemiology information, risk factors, and racial differences in PCa diagnosis, current status and new trends in surgery management and novel agents for castration-resistant prostate cancer. We believe such information would be helpful in clinical decision making for urologists and oncologists, health-care ministries and medical researchers.
Keywords: Asian population; Epidemiology; Prostate cancer; Racial differences; Risk factors; Surgery management.
Figures



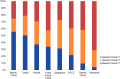


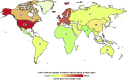

References
-
- Siegel R., Naishadham D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Center M.M., Jemal A., Lortet-Tieulent J., Ward E., Ferlay J., Brawley O. International variation in prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates. Eur Urol. 2012;61:1079–1092. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J.S.I., Ervik M., Dikshit R., Eser S., Mathers C., Rebelo M. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2013. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11.http://globocan.iarc.fr [Internet] Available from: [accessed 28.08.14]
-
- Pramesh C.S., Badwe R.A., Borthakur B.B., Chandra M., Raj E.H., Kannan T. Delivery of affordable and equitable cancer care in India. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e223–e233. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A., Bray F., Center M.M., Ferlay J., Ward E., Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

