Effects of regular-moderate exercise on high-fat diet-induced intramyocellular lipid accumulation in the soleus muscle of Sprague-Dawley rats
- PMID: 29511650
- PMCID: PMC5833965
- DOI: 10.12965/jer.1835166.583
Effects of regular-moderate exercise on high-fat diet-induced intramyocellular lipid accumulation in the soleus muscle of Sprague-Dawley rats
Abstract
Previously, we monitored the expression level of the pro-apoptotic proteins caspase-3 and cleaved poly-ADP-ribose polymerase in the skeletal muscle of high-fat diet-induced obese rats in order to assess muscle damage. In this study, we analyzed whether exercise or dietary adjustment was more effective at preventing high-fat diet-induced muscle damage. High-fat diet-induced obese rats were divided into three groups: the high-fat diet (HFD), the combined high-fat diet and exercise (HFD+EXE), and the dietary adjustment (DA) groups. For 6 weeks, the HFD+EXE group was subjected to exercise on an animal treadmill. Capsase-3 protein was quantified, and histopathology of the soleus muscle was performed. Both the HFD+EXE and DA interventions resulted in a reduction of lipid accumulation in the soleus muscle, and nucleus infiltration was significantly lower in the DA group. The inflammatory response, caspase-3 level, and relative muscle weight were significantly higher in the HFD+EXE group compared to the HFD group. An increase in intramyocellular lipids in the soleus muscle by obesity and exercise stimulated apoptosis. When the rats exercised, muscle growth was normal and unrelated to the effects of lipid accumulation. These data indicate that exercise was more effective than dietary adjustment in reducing lipid accumulation and increasing muscle metabolism.
Keywords: Cell damage; High-fat diet; Lipid accumulation; Obesity; Regular-moderate exercise; Skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


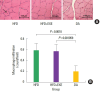

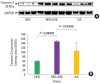
References
-
- Baek KW, Cha HJ, Park JJ. Effects of high-fat diet on type-I muscle loss in rats. J Life Sci. 2013;23:1509–1515.
-
- Bastie CC, Hajri T, Drover VA, Grimaldi PA, Abumrad NA. CD36 in myocytes channels fatty acids to a lipase-accessible triglyceride pool that is related to cell lipid and insulin responsiveness. Diabetes. 2004;53:2209–2216. - PubMed
-
- Boor P, Celec P, Behuliak M, Grancic P, Kebis A, Kukan M, Pronayová N, Liptaj T, Ostendorf T, Sebeková K. Regular moderate exercise reduces advanced glycation and ameliorates early diabetic nephropathy in obese Zucker rats. Metabolism. 2009;58:1669–1677. - PubMed
-
- Borghouts LB, Keizer HA. Exercise and insulin sensitivity: a review. Int J Sports Med. 2000;21:1–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

