Ethanol Extract from Ulva prolifera Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation Response in Mice
- PMID: 29511669
- PMCID: PMC5817197
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/1374565
Ethanol Extract from Ulva prolifera Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation Response in Mice
Abstract
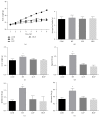
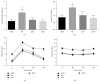
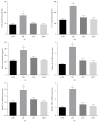
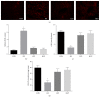
Ulva prolifera is the major causative species in the green tide, a serious marine ecological disaster, which bloomed in the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea of China. However, it is also a popular edible seaweed and its extracts exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. The present study investigated the effects of ethanol extract of U. prolifera (EUP) on insulin sensitivity, inflammatory response, and oxidative stress in high-fat-diet- (HFD-) treated mice. HFD-treated mice obtained drinking water containing 2% or 5% EUP. The results showed that EUP supplementation significantly prevented HFD-induced weight gain of liver and fat. EUP supplementation also improved glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in HFD-treated mice. Moreover, EUP supplementation prevented the increased expression of genes involved in triglyceride synthesis and proinflammatory genes and the decreased expression of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation in liver of HFD-treated mice. Furthermore, EUP supplementation decreased reactive oxygen species content, while increasing glutathione content and glutathione peroxidase activity in HFD-treated mice. In conclusion, our results showed that EUP improved insulin resistance and had antilipid accumulation and anti-inflammatory and antioxidative effects on HFD-treated mice. We suggested that U. prolifera extracts may be regarded as potential candidate for the prevention of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pu-erh tea extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and insulin resistance by modulating hepatic IL-6/STAT3 signaling in mice.J Gastroenterol. 2016 Aug;51(8):819-29. doi: 10.1007/s00535-015-1154-0. Epub 2016 Jan 21. J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26794005
-
SARM1 deletion restrains NAFLD induced by high fat diet (HFD) through reducing inflammation, oxidative stress and lipid accumulation.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Apr 6;498(3):416-423. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.115. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29454967
-
Hydroxytyrosol prevents reduction in liver activity of Δ-5 and Δ-6 desaturases, oxidative stress, and depletion in long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid content in different tissues of high-fat diet fed mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Apr 11;16(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0450-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28395666 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamin ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in rats on a high-fat diet via LXRα and PPARα.Nutr Res. 2016 Sep;36(9):1022-1030. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2016.06.015. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Nutr Res. 2016. PMID: 27632923
-
Genetic evidence in tracking the origin of Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea, China.Harmful Algae. 2018 Sep;78:86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Harmful Algae. 2018. PMID: 30196928 Review.
Cited by
-
Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Hepatic Lipogenesis and Inflammation.Mar Drugs. 2020 Sep 18;18(9):475. doi: 10.3390/md18090475. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32962167 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Microalgae and Macroalgae Extracts on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 11;13(6):2017. doi: 10.3390/nu13062017. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34208211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation and Characterization of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Enteromorpha prolifera Lipids and Their Preventive Effects on Ulcerative Colitis in C57BL/6J Mice.Foods. 2023 Dec 21;13(1):46. doi: 10.3390/foods13010046. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38201073 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic effect of fucoxanthin extracted from Sargassum angustifolium on streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetic mice.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 May 6;9(7):3521-3529. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2301. eCollection 2021 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34262712 Free PMC article.
-
Ulva prolifera Polysaccharide-Manganese Alleviates Inflammation and Regulates Microbiota Composition in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis Mice.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 24;13:916552. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.916552. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35722338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z., Xiao J., Fan S., Li Y., Liu X., Liu D. Who made the world’s largest green tide in china?—an integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in yellow sea. Limnology and Oceanography. 2015;60(4):1105–1117. doi: 10.1002/lno.10083. - DOI
-
- Song W., Li Y., Fang S., et al. Temporal and spatial distributions of green algae micro-propagules in the coastal waters of the Subei Shoal, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 2015;163:29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.08.006. - DOI
-
- Song W., Peng K., Xiao J., et al. Effects of temperature on the germination of green algae micro-propagules in coastal waters of the Subei Shoal, China. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 2015;163:63–68. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.08.007. - DOI
-
- Liu D., Keesing J. K., He P., Wang Z., Shi Y., Wang Y. The world's largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 2013;129:2–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2013.05.021. - DOI
-
- Ye H., Zhou C., Sun Y., et al. Antioxidant activities in vitro of ethanol extract from brown seaweed Sargassum pallidum. European Food Research and Technology. 2009;230(1):101–109. doi: 10.1007/s00217-009-1147-4. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

