Overexpression of adrenomedullin protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia and serum deprivation‑induced apoptosis via the Akt/GSK3β and Bcl‑2 signaling pathways
- PMID: 29512737
- PMCID: PMC5881801
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3533
Overexpression of adrenomedullin protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia and serum deprivation‑induced apoptosis via the Akt/GSK3β and Bcl‑2 signaling pathways
Abstract
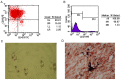
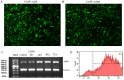
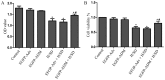
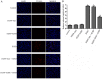
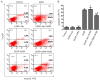
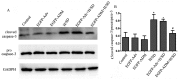
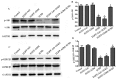
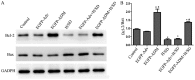
The poor survival rate of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) within the ischemic heart limits their therapeutic potential for cardiac repair. Adrenomedullin (ADM) has been identified as a potent apoptotic inhibitor. The present study aimed to investigate the protective effects of ADM on MSCs against hypoxia and serum deprivation (H/SD)‑induced apoptosis, and to determine the potential underlying mechanisms. In the present study, a recombinant adenovirus expressing the ADM gene was established and was infected into MSCs. The infection rate was determined via microscopic detection of green fluorescence and flow cytometric analysis. The mRNA expression levels of ADM were detected by reverse transcription‑polymerase chain reaction. In addition, a model of H/SD was generated. The MSCs were randomly separated into six groups: Control, enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)‑Adv, EGFP‑ADM, H/SD, EGFP‑Adv + H/SD and EGFP‑ADM + H/SD. Cell viability and proliferation were determined using the Cell Counting kit‑8 assay. Apoptosis was assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase‑mediated‑dUTP nick‑end labeling assay and flow cytometric analysis using Annexin V‑phycoerythrin/7‑aminoactinomycin D staining. The protein expression levels of total protein kinase B (Akt), phosphorylated (p)‑Akt, total glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)3β, p‑GSK3β, B‑cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‑2), Bcl‑2‑associated X protein (Bax), caspase‑3 and cleaved caspase‑3 were detected by western blot analysis. The results indicated that ADM overexpression could improve MSC proliferation and viability, and protect MSCs against H/SD‑induced apoptosis. In addition, ADM overexpression increased Akt and GSK3β phosphorylation, and Bcl‑2/Bax ratio, and decreased the activation of caspase‑3. These results suggested that ADM protects MSCs against H/SD‑induced apoptosis, which may be mediated via the Akt/GSK3β and Bcl‑2 signaling pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Jan;33(1):97-104. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1550. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24212403
-
Effects of dexmedetomidine postconditioning on myocardial ischemia and the role of the PI3K/Akt-dependent signaling pathway in reperfusion injury.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jul;14(1):797-803. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5345. Epub 2016 May 24. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27221008 Free PMC article.
-
PBX homeobox 1 enhances hair follicle mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and reprogramming through activation of the AKT/glycogen synthase kinase signaling pathway and suppression of apoptosis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Aug 23;10(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1382-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31443676 Free PMC article.
-
Omentin-1 effects on mesenchymal stem cells: proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Oct 10;8(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0676-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29017592 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E₁ protects bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells against serum deprivation-induced apoptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Oct;12(4):5723-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4176. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26252504 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adrenomedullin and Protecting Spinal Motor Neurons Against Doxorubicin-induced Toxicity.Basic Clin Neurosci. 2024 Sep-Oct;15(5):617-630. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2022.3650.1. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 40583883 Free PMC article.
-
c-Abl Tyrosine Kinase-Mediated Neuronal Apoptosis in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Modulating the LRP-1-Dependent Akt/GSK3β Survival Pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2021 Dec;71(12):2514-2525. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01835-5. Epub 2021 Mar 30. J Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33786723
-
Low-Frequency Magnetic Fields (LF-MFs) Inhibit Proliferation by Triggering Apoptosis and Altering Cell Cycle Distribution in Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 22;21(8):2952. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082952. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32331350 Free PMC article.
-
Human Trophoblast Differentiation Is Associated With Profound Gene Regulatory and Epigenetic Changes.Endocrinology. 2019 Sep 1;160(9):2189-2203. doi: 10.1210/en.2019-00144. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 31294776 Free PMC article.
-
Non-cytotoxic doses of shikonin inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α expression via activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Nov;20(5):45. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9173. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32952636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rouhi L, Kajbafzadeh AM, Modaresi M, Shariati M, Hamrahi D. Autologous serum enhances cardiomyocyte differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the presence of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013;49:287–294. doi: 10.1007/s11626-013-9597-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ishimine H, Yamakawa N, Sasao M, Tadokoro M, Kami D, Komazaki S, Tokuhara M, Takada H, Ito Y, Kuno S, et al. N-Cadherin is a prospective cell surface marker of human mesenchymal stem cells that have high ability for cardiomyocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;438:753–759. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.081. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mathiasen AB, Qayyum AA, Jørgensen E, Helqvist S, Fischer-Nielsen A, Kofoed KF, Haack-Sørensen M, Ekblond A, Kastrup J. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cell treatment in patients with severe ischaemic heart failure: A randomized placebo-controlled trial (MSC-HF trial) Eur Heart J. 2015;36:1744–1753. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv136. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

