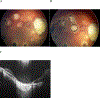
Intravitreal chemotherapy and laser for newly visible subretinal seeds in retinoblastoma
- PMID: 29513055
- PMCID: PMC7432965
- DOI: 10.1080/13816810.2018.1443343
Intravitreal chemotherapy and laser for newly visible subretinal seeds in retinoblastoma
Abstract
Background: There has been no effective method for treating newly visible ("new") subretinal seeding in retinoblastoma except enucleation. The objective of this report is to determine whether intravitreal chemotherapy combined with 810 nm indirect laser can successfully treat retinoblastoma eyes with "new" subretinal seeding which appeared after intra-arterial chemotherapy (ophthalmic arterial chemosurgery: OAC).
Material and methods: Single center retrospective study from a tertiary cancer hospital of a case series of 14 eyes treated with combined intravitreal chemotherapy and laser from 2012 to 2017. Ocular salvage, patient survival, recurrence-free ocular survival, metastases, and extraocular extension were assessed.
Results: A total of 14 eyes in 13 unilateral or bilateral retinoblastoma patients with "new" subretinal seeding after initial eye salvage therapy were treated with combined intravitreal injection of melphalan (30 ug) or melphalan (30 ug) and topotecan (20 ug) and with 810 nm indirect continuous wave laser. All eyes were salvaged. Only two eyes (14%) recurred again for subretinal seeds after 6 and 8 months, respectively, and required additional cycles of intravitreal injections and laser. Combined intravitreal injection of melphalan or melphalan plus topotecan with 810 nm indirect continuous wave laser was not associated with any metastatic events, patient deaths, extraocular extension, or need for enucleation.
Conclusion: There has been no effective treatment for "new" subretinal seeding after OAC except enucleation or second course OAC. Combined intravitreal chemotherapy with 810 nm indirect laser may be an effective and safe alternative to enucleation.
Keywords: Intravitreal chemotherapy; laser; newly visible subretinal seeds; ocular salvage; retinoblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Reese AB. Retinoblastoma: past, present and future. Bibl Ophthalmol. 1968;75:138–141. - PubMed
-
- Abramson DH. Retinoblastoma: saving life with vision. Annu Rev Med. 2014;65(1):171–184. - PubMed
-
- Abramson DH, Marr BP, Dunkel IJ, et al. Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma in eyes with vitreous and/or subretinal seeding: 2-year results. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96(4):499–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources