Electrochemical and surface plasmon insulin assays on clinical samples
- PMID: 29513312
- PMCID: PMC5869170
- DOI: 10.1039/c7an01872j
Electrochemical and surface plasmon insulin assays on clinical samples
Abstract
Diabetes is a complex immune disorder that requires extensive medical care beyond glycemic control. Recently, the prevalence of diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes (T1D), has significantly increased from 5% to 10%, and this has affected the health-associated complication incidences in children and adults. The 2012 statistics by the American Diabetes Association reported that 29.1 million Americans (9.3% of the population) had diabetes, and 86 million Americans (age ≥20 years, an increase from 79 million in 2010) had prediabetes. Personalized glucometers allow diabetes management by easy monitoring of the high millimolar blood glucose levels. In contrast, non-glucose diabetes biomarkers, which have gained considerable attention for early prediction and provide insights about diabetes metabolic pathways, are difficult to measure because of their ultra-low levels in blood. Similarly, insulin pumps, sensors, and insulin monitoring systems are of considerable biomedical significance due to their ever-increasing need for managing diabetic, prediabetic, and pancreatic disorders. Our laboratory focuses on developing electrochemical immunosensors and surface plasmon microarrays for minimally invasive insulin measurements in clinical sample matrices. By utilizing antibodies or aptamers as the insulin-selective biorecognition elements in combination with nanomaterials, we demonstrated a series of selective and clinically sensitive electrochemical and surface plasmon immunoassays. This review provides an overview of different electrochemical and surface plasmon immunoassays for insulin. Considering the paramount importance of diabetes diagnosis, treatment, and management and insulin pumps and monitoring devices with focus on both T1D (insulin-deficient condition) and type 2 diabetes (insulin-resistant condition), this review on insulin bioassays is timely and significant.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



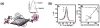

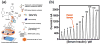

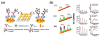
Similar articles
-
The effectiveness of continuous subcutaneous insulin pumps with continuous glucose monitoring in outpatient adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-10. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-170. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820140
-
Recent advances in biosensor technology in assessment of early diabetes biomarkers.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Jan 15;99:122-135. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.047. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 28750336 Review.
-
Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) Pumps for Type 1 and Type 2 Adult Diabetic Populations: An Evidence-Based Analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(20):1-58. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074525 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic/Immunoassay Dual-Biomarker Sensing Chip: Towards Decentralized Insulin/Glucose Detection.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 May 6;58(19):6376-6379. doi: 10.1002/anie.201902664. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 30868724
-
Diabetes technology and treatments in the paediatric age group.Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011 Feb;(170):76-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2010.02582.x. Int J Clin Pract Suppl. 2011. PMID: 21323816 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Nanostructured Aptasensor for Direct Detection of Glycated Hemoglobin.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 24;26(15):7140. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157140. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806272 Free PMC article.
-
Building Biomimetic Potency Tests for Islet Transplantation.Diabetes. 2021 Feb;70(2):347-363. doi: 10.2337/db20-0297. Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 33472944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A colorimetric sensing strategy based on chitosan-stabilized platinum nanoparticles for quick detection of α-glucosidase activity and inhibitor screening.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024 Nov;416(27):6001-6010. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05198-9. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2024. PMID: 38358531
-
Immunosensors for Autoimmune-Disease-Related Biomarkers: A Literature Review.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;23(15):6770. doi: 10.3390/s23156770. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microliter Sample Insulin Detection Using a Screen-Printed Electrode Modified by Nickel Hydroxide.ACS Omega. 2020 Mar 10;5(11):6169-6176. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00194. eCollection 2020 Mar 24. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32226901 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

