Comparison of neuroprotective efficacy of poly-arginine R18 and R18D (D-enantiomer) peptides following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the Wistar rat and in vitro toxicity studies
- PMID: 29513757
- PMCID: PMC5841795
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193884
Comparison of neuroprotective efficacy of poly-arginine R18 and R18D (D-enantiomer) peptides following permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the Wistar rat and in vitro toxicity studies
Abstract
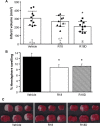
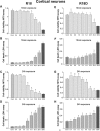
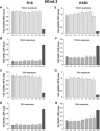
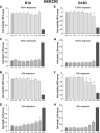
We have previously demonstrated that arginine-rich and poly-arginine peptides possess potent neuroprotective properties, with poly-arginine peptide R18 identified as being highly effective at reducing infarct volume following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in the Sprague Dawley rat. Since peptides synthesised using D-isoform amino acids have greater stability than L-isoform peptides due to increased resistance to proteolytic degradation, they represent potentially more effective peptide therapeutics. Therefore we compared the neuroprotective efficacy of R18 and its D-enantiomer R18D following permanent MCAO in the Wistar rat. Furthermore, as increased peptide stability may also increase peptide toxicity, we examined the effects of R18 and R18D on cultured cortical neurons, astrocytes, brain endothelial cells (bEND.3), and embryonic kidney cells (HEK293) following a 10-minute or 24-hour peptide exposure duration. The in vivo studies demonstrated that R18D resulted in a greater reduction in mean infarct volume compared to R18 (33%, p = 0.004 vs 12%, p = 0.27) after intravenous administration at 300 nmol/kg 30 minutes after MCAO. Both R18D and R18 reduced cerebral hemisphere swelling to a comparable degree (27%, p = 0.03 and 30%, p = 0.02), and improved neurological assessment scores (1.5, p = 0.02 and 2, p = 0.058 vs 3 for vehicle). No abnormal histological findings specific to peptide treatments were observed in hematoxylin and eosin stained sections of kidney, liver, spleen, lung and heart. In vitro studies demonstrated that R18 and R18D were most toxic to neurons, followed by astrocytes, HEK293 and bEND.3 cells, but only at high concentrations and/or following 24-hour exposure. These findings further highlight the neuroprotective properties of poly-arginine peptides, and indicate that R18D at the dose examined is more potent than R18 in Wistar rats, and justify continued investigation of the R18 peptide as a novel neuroprotective agent for stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative Assessment of the Proteolytic Stability and Impact of Poly-Arginine Peptides R18 and R18D on Infarct Growth and Penumbral Tissue Preservation Following Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in the Sprague Dawley Rat.Neurochem Res. 2021 May;46(5):1166-1176. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03251-y. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 33523394
-
Assessment of the Neuroprotective Effects of Arginine-Rich Protamine Peptides, Poly-Arginine Peptides (R12-Cyclic, R22) and Arginine-Tryptophan-Containing Peptides Following In Vitro Excitotoxicity and/or Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Rats.Neuromolecular Med. 2017 Sep;19(2-3):271-285. doi: 10.1007/s12017-017-8441-2. Epub 2017 May 18. Neuromolecular Med. 2017. PMID: 28523591
-
Poly-arginine R18 and R18D (D-enantiomer) peptides reduce infarct volume and improves behavioural outcomes following perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy in the P7 rat.Mol Brain. 2018 Feb 9;11(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13041-018-0352-0. Mol Brain. 2018. PMID: 29426351 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective peptides fused to arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides: Neuroprotective mechanism likely mediated by peptide endocytic properties.Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Sep;153:36-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.06.002. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26048328 Review.
-
Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and Neuroprotective Peptide Therapies: A Case for Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs).Brain Sci. 2018 Aug 7;8(8):147. doi: 10.3390/brainsci8080147. Brain Sci. 2018. PMID: 30087289 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of microRNA-29b suppresses oxidative stress and reduces apoptosis in ischemic stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Feb;17(2):433-439. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.314319. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 34269220 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in D-Amino Acids in Neurological Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 3;21(19):7325. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197325. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly-arginine-18 (R18) Confers Neuroprotection through Glutamate Receptor Modulation, Intracellular Calcium Reduction, and Preservation of Mitochondrial Function.Molecules. 2020 Jun 29;25(13):2977. doi: 10.3390/molecules25132977. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32610439 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the safety of the cationic arginine-rich peptides (CARPs) poly-arginine-18 (R18 and R18D) in ex vivo models of mast cell degranulation and red blood cell hemolysis.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Jul 1;31:101305. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101305. eCollection 2022 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 35812346 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of poly-arginine R18 on neurocyte cell growth via autophagy in traumatic brain injury.Exp Ther Med. 2019 May;17(5):4109-4115. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7423. Epub 2019 Mar 20. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30988787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meloni BP, Craig AJ, Milech N, Hopkins RM, Watt PM, Knuckey NW. The neuroprotective efficacy of cell-penetrating peptides TAT, penetratin, Arg-9, and Pep-1 in glutamic acid, kainic acid, and in vitro ischemia injury models using primary cortical neuronal cultures. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2014; 34: 173–181. doi: 10.1007/s10571-013-9999-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meloni BP, Brookes LM, Clark VW, Cross JL, Edwards AB, Anderton RS, et al. Poly-arginine and arginine-rich peptides are neuroprotective in stroke models. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015; 35: 993–1004. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Meloni BP, Milani D, Edwards AB, Anderton RS, O'Hare Doig RL, et al. Neuroprotective peptides fused to arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides: Neuroprotective mechanism likely mediated by peptide endocytic properties. Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 153: 36–54. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.06.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meloni BP, Milani D, Cross JL, Clark VW, Edwards AB, Anderton RS, et al. Assessment of the neuroprotective effects of arginine-rich protamine peptides, poly-arginine peptides (R12-cylic, R22) and arginine-tryptophan containing peptides following in vitro excitotoxicity and/or permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neuromol Med. 2017; 19: 271–285. - PubMed
-
- Milani D, Clark VW, Cross JL, Anderton RS, Knuckey NW, Meloni BP. Poly-arginine peptides reduce infarct volume in a permanent middle cerebral artery rat stroke model. BMC Neurosci. 2016; 17: 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0236-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

