Expression profile of endothelin receptors (ETA and ETB) and microRNAs-155 and -199 in the corpus cavernosum of rats submitted to chronic alcoholism and diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 29513879
- PMCID: PMC5912101
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X20176329
Expression profile of endothelin receptors (ETA and ETB) and microRNAs-155 and -199 in the corpus cavernosum of rats submitted to chronic alcoholism and diabetes mellitus
Abstract
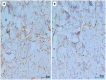
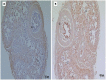
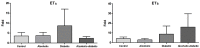
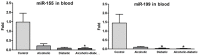
Recent evidence shows that chronic ethanol consumption increases endothelin (ET)-1 induced sustained contraction of trabecular smooth muscle cells of the corpora cavernosa in corpus cavernosum of rats by a mechanism that involves increased expression of ETA and ETB receptors. Our goal was to evaluate the effects of alcohol and diabetes and their relationship to miRNA-155, miRNA-199 and endothelin receptors in the corpus cavernosum and blood of rats submitted to the experimental model of diabetes mellitus and chronic alcoholism. Forty-eight male Wistar rats were divided into four groups: control (C), alcoholic (A), diabetic (D), and alcoholic-diabetic (AD). Samples of the corpus cavernosum were prepared to study the protein expression of endothelin receptors by immunohistochemistry and expression of miRNAs-155 and -199 in serum and the cavernous tissue. Immunostaining for endothelin receptors was markedly higher in the A, D, and AD groups than in the C group. Moreover, a significant hypoexpression of the miRNA-199 in the corpus cavernosum tissue from the AD group was observed, compared to the C group. When analyzing the microRNA profile in blood, a significant hypoexpression of miRNA-155 in the AD group was observed compared to the C group. The miRNA-199 analysis demonstrated significant hypoexpression in D and AD groups compared to the C group. Our findings in corpus cavernosum showed downregulated miRNA-155 and miRNA-199 levels associated with upregulated protein expression and unaltered mRNA expression of ET receptors suggesting decreased ET receptor turnover, which can contribute to erectile dysfunction in diabetic rats exposed to high alcohol levels.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Morphological and molecular analysis of apoptosis in the corpus cavernosum of rats submitted to a chronic alcoholism model.Acta Cir Bras. 2020 Jun 3;35(3):e202000305. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020200030000005. eCollection 2020. Acta Cir Bras. 2020. PMID: 32520081 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiles of eNOS, iNOS and microRNA-27b in the corpus cavernosum of rats submitted to chronic alcoholism and Diabetes mellitus.Acta Cir Bras. 2017 Jan;32(1):38-45. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020170105. Acta Cir Bras. 2017. PMID: 28225916
-
Alterations in endothelin B receptor sites in cavernosal tissue of diabetic rabbits: potential relevance to the pathogenesis of erectile dysfunction.J Urol. 1997 Nov;158(5):1966-72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(01)64195-8. J Urol. 1997. PMID: 9334651
-
Ethanol consumption increases endothelin-1 expression and reactivity in the rat cavernosal smooth muscle.Alcohol Alcohol. 2013 Nov-Dec;48(6):657-66. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agt057. Epub 2013 Jun 23. Alcohol Alcohol. 2013. PMID: 23797280
-
[Phenotype modulation of smooth muscle in corpus cavernosum in penis tunica albuginea in diabetes mellitus with erectile dysfunction: experiment with rats].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Nov 13;87(42):3006-11. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18261337 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNAs: New Dawn for Diabetes Mellitus Induced Erectile Dysfunction.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 22;9:888624. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.888624. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35813828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological and molecular analysis of apoptosis in the corpus cavernosum of rats submitted to a chronic alcoholism model.Acta Cir Bras. 2020 Jun 3;35(3):e202000305. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020200030000005. eCollection 2020. Acta Cir Bras. 2020. PMID: 32520081 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-383 suppresses oxidative stress and improves endothelial function by increasing sirtuin 1.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020 Jan 24;53(2):e8616. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20198616. eCollection 2020. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 31994599 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehension of gut microbiota and microRNAs may contribute to the development of innovative treatment tactics against metabolic disorders and psychiatric disorders.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 25;16(6):111-125. doi: 10.62347/WAZH2090. eCollection 2024. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39850247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic liver diseases and erectile dysfunction.Front Public Health. 2023 Jan 6;10:1092353. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1092353. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36684968 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Impotence NIH Consens Statement. 1992;10:1–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

