Estrogen Deficiency Promotes Hepatic Steatosis via a Glucocorticoid Receptor-Dependent Mechanism in Mice
- PMID: 29514097
- PMCID: PMC5875726
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.041
Estrogen Deficiency Promotes Hepatic Steatosis via a Glucocorticoid Receptor-Dependent Mechanism in Mice
Abstract
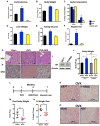
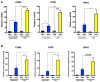
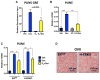
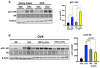
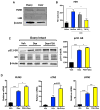
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are master regulators of systemic metabolism. Intriguingly, Cushing's syndrome, a disorder of excessive GCs, phenocopies several menopause-induced metabolic pathologies. Here, we show that the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) drives steatosis in hypogonadal female mice because hepatocyte-specific GR knockout mice are refractory to developing ovariectomy-induced steatosis. Intriguingly, transcriptional profiling revealed that ovariectomy elicits hepatic GC hypersensitivity globally. Hypogonadism-induced GC hypersensitivity results from a loss of systemic but not hepatic estrogen (E2) signaling, given that hepatocyte-specific E2 receptor deletion does not confer GC hypersensitivity. Mechanistically, enhanced chromatin recruitment and ligand-dependent hyperphosphorylation of GR underlie ovariectomy-induced glucocorticoid hypersensitivity. The dysregulated glucocorticoid-mediated signaling present in hypogonadal females is a product of increased follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) production because FSH treatment in ovary-intact mice recapitulates glucocorticoid hypersensitivity similar to hypogonadal female mice. Our findings uncover a regulatory axis between estradiol, FSH, and hepatic glucocorticoid receptor signaling that, when disrupted, as in menopause, promotes hepatic steatosis.
Keywords: estrogen receptor; follicle-stimulating hormone; glucocorticoid receptor; lipid metabolism; liver; menopause; metabolic syndrome; steatosis.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Arnaldi G, Scandali VM, Trementino L, Cardinaletti M, Appolloni G, Boscaro M. Pathophysiology of dyslipidemia in Cushing’s syndrome. Neuroendocrinology. 2010;92(Suppl 1):86–90. - PubMed
-
- Bingol B, Gunenc Z, Yilmaz M, Biri A, Tiras B, Güner H. Effects of hormone replacement therapy on glucose and lipid profiles and on cardiovascular risk parameters in postmenopausal women. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2010;281:857–864. - PubMed
-
- Bougarne N, Paumelle R, Caron S, Hennuyer N, Mansouri R, Gervois P, Staels B, Haegeman G, De Bosscher K. PPARalpha blocks glucocorticoid receptor alpha-mediated transactivation but cooperates with the activated glucocorticoid receptor alpha for transrepression on NF-kappaB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:7397–7402. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

