Real-World Scenario Improvements in Serum Phosphorus Levels and Pill Burden in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients Treated with Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide
- PMID: 29514139
- PMCID: PMC5906196
- DOI: 10.1159/000487856
Real-World Scenario Improvements in Serum Phosphorus Levels and Pill Burden in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients Treated with Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide
Abstract
Background: A database analysis was conducted to assess the effectiveness of sucroferric oxyhydroxide (SO) on lowering serum phosphorus and phosphate binder (PB) pill burden among adult peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients prescribed SO as part of routine care.
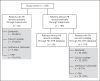
Methods: Adult PD patients (n = 258) prescribed SO through a renal pharmacy service were analyzed. Baseline was 3 months before SO prescription. SO-treated follow-up was for 6 months or until either a new PB was prescribed, SO was not refilled, PD modality changed, or patient was discharged. In-range serum phosphorus was defined as ≤5.5 mg/dL.
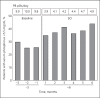
Results: At baseline, mean serum phosphorus was 6.59 mg/dL with 10 prescribed PB pills/day. The proportion of patients achieving in-range serum phosphorus increased by 72% from baseline to month 6. Prescribed PB pills/day decreased by 57% (10 at baseline to 4.3 at SO follow-up, p < 0.0001). The mean length of SO follow-up was 5.1 months; SO follow-up ended for 38, 27, and 50 patients at months 4, 5, and 6, respectively, due to no further PB fills, and for 10, 11, and 4 patients at months 4, 5, and 6, respectively, due to another PB prescribed. In patients with baseline serum phosphorus >5.5 mg/dL who achieved in-range serum phosphorus during SO follow-up for ≥1 quarter, a notable improvement in serum phosphorus (6.54 to 5.10 mg/dL, p < 0.0001) was observed, and there was a 53% reduction in PB pill burden (9.9 to 4.7, p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Among PD patients prescribed SO as part of routine care, improvements in serum phosphorus control and >50% reduction in PB pills/day were observed.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorders; Peritoneal Dialysis; Phosphate binders; Phosphorus.
The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide for hyperphosphatemia: a review of real-world evidence.J Nephrol. 2022 Apr;35(3):875-888. doi: 10.1007/s40620-021-01241-5. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35138627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The real-world effectiveness of sucroferric oxyhydroxide in European hemodialysis patients: a 1-year retrospective database analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Dec 7;21(1):530. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02188-8. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33287733 Free PMC article.
-
Management of serum phosphorus over a 1-year follow-up in patients on peritoneal dialysis prescribed sucroferric oxyhydroxide as part of routine care: a retrospective analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Jun 17;25(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03633-8. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38886636 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world effectiveness of sucroferric oxyhydroxide in patients on chronic hemodialysis: A retrospective analysis of pharmacy data .Clin Nephrol. 2017 Aug;88(8):59-67. doi: 10.5414/CN109021. Clin Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28587714 Free PMC article.
-
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide for the treatment of hyperphosphatemia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;19(10):1137-1148. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2018.1491548. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29985725 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperphosphatemia and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Major Daily Concern Both in Adults and in Children.Calcif Tissue Int. 2021 Jan;108(1):116-127. doi: 10.1007/s00223-020-00665-8. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Calcif Tissue Int. 2021. PMID: 31996964 Review.
-
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide for hyperphosphatemia: a review of real-world evidence.J Nephrol. 2022 Apr;35(3):875-888. doi: 10.1007/s40620-021-01241-5. Epub 2022 Feb 9. J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35138627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A real-world analysis of the influence of age on maintenance hemodialysis patients: managing serum phosphorus with sucroferric oxyhydroxide as part of routine clinical care.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Feb;55(2):377-387. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03327-w. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 35953565 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world management of hyperphosphataemia with sucroferric oxyhydroxide: the VELREAL multicentre study.Clin Kidney J. 2021 Feb 1;14(2):681-687. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa226. eCollection 2021 Feb. Clin Kidney J. 2021. PMID: 33626111 Free PMC article.
-
The real-world effectiveness of sucroferric oxyhydroxide in European hemodialysis patients: a 1-year retrospective database analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Dec 7;21(1):530. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02188-8. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33287733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klarenbach SW, Tonelli M, Chui B, Manns BJ. Economic evaluation of dialysis therapies. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10:644–652. - PubMed
-
- Rubin HR, Fink NE, Plantinga LC, Sadler JH, Kliger AS, Powe NR. Patient ratings of dialysis care with peritoneal dialysis vs hemodialysis. JAMA. 2004;291:697–703. - PubMed
-
- United States Renal Data System 2016 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2016
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

