The Continuing Burden of Advanced HIV Disease Over 10 Years of Increasing Antiretroviral Therapy Coverage in South Africa
- PMID: 29514233
- PMCID: PMC5850025
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix1140
The Continuing Burden of Advanced HIV Disease Over 10 Years of Increasing Antiretroviral Therapy Coverage in South Africa
Abstract
Background: Antiretroviral treatment (ART) has been massively scaled up to decrease human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related morbidity, mortality, and HIV transmission. However, despite documented increases in ART coverage, morbidity and mortality have remained substantial. This study describes trends in the numbers and characteristics of patients with very advanced HIV disease in the Western Cape, South Africa.
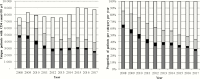
Methods: Annual cross-sectional snapshots of CD4 distributions were described over 10 years, derived from a province-wide cohort of all HIV patients receiving CD4 cell count testing in the public sector. Patients with a first CD4 count <50 cells/µL in each year were characterized with respect to prior CD4 and viral load testing, ART access, and retention in ART care.
Results: Patients attending HIV care for the first time initially constituted the largest group of those with CD4 count <50 cells/µL, dropping proportionally over the decade from 60.9% to 26.7%. By contrast, the proportion who were ART experienced increased from 14.3% to 56.7%. In patients with CD4 counts <50 cells/µL in 2016, 51.8% were ART experienced, of whom 76% could be confirmed to be off ART or had recent viremia. More than half who were ART experienced with a CD4 count <50 cells/µL in 2016 were men, compared to approximately one-third of all patients on ART in the same year.
Conclusions: Ongoing HIV-associated morbidity now results largely from treatment-experienced patients not being in continuous care or not being fully virologically suppressed. Innovative interventions to retain ART patients in effective care are an essential priority for the ongoing HIV response.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Progress report 2016, Prevent HIV, Test and Treat All, WHO support for country impact. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2016.
-
- World Health Organization/Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. Treating 3 million people living with HIV/AIDS by 2005: Making it Happen: the WHO strategy. The WHO and UNAIDS global initiative to provide antiretroviral therapy to 3 million people with HIV/AIDS in developing countries by the end of 2005. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2004.
-
- World Health Organization. Rapid advice: antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection in adults and adolescents. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2009.
-
- World Health Organization. Consolidated guidelines on the use of antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection: recommendations for a public health approach. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2013:272. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Guideline on when to start antiretroviral therapy and on pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO, 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

