Effects of dietary protein sources and nisin on rumen fermentation, nutrient digestion, plasma metabolites, nitrogen utilization, and growth performance in growing lambs
- PMID: 29514293
- PMCID: PMC6140948
- DOI: 10.1093/jas/sky086
Effects of dietary protein sources and nisin on rumen fermentation, nutrient digestion, plasma metabolites, nitrogen utilization, and growth performance in growing lambs
Abstract
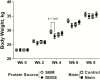
This study investigated the effects of dietary protein sources and nisin on rumen fermentation, nutrient digestion, plasma metabolites, N utilization, and growth performance in growing lambs. Thirty-two male Hu lambs (23 ± 2 kg initial BW) were assigned to four dietary treatments in a randomized block design with a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement. Two protein sources, soybean meal (SBM) and dried distillers grains with solubles (DDGS), and two levels of nisin, 0 and 30.5 mg of nisin/kg of feed, were used to formulate four isonitrogenous and isoenergetic diets. No interaction (P ≥ 0.16) of protein × nisin was found except on apparent digestibility of DM, OM, NDF, and ADF (P ≤ 0.02). Lambs receiving DDGS had lower (P ≤ 0.04) concentrations of ruminal acetate and butyrate, but propionate concentrations did not differ (P = 0.39), compared with those fed SBM, leading to a trend for reduced total VFA concentration (P = 0.07). Ruminal NH3-N and total branched-chain VFA concentrations were lower (P ≤ 0.01) in the lambs fed DDGS than in those fed SBM. The DDGS-fed lambs had less (P < 0.01) CP, but greater (P < 0.01) ether extract apparent digestibility than those fed SBM. For plasma metabolites, only blood urea N and albumin concentrations were lower in the DDGS-fed lambs (P < 0.01) than in those fed SBM. Nitrogen excretion pathway was altered when DDGS replaced SBM, with fecal N excretion (% of N intake) being greater (P < 0.01), while urinary N excretion (% of N intake) tending to be less (P = 0.06) from the DDGS-fed lambs than those fed SBM. Protein sources affected growth performance in an age/time-dependent manner. From weeks 1 to 4, DDGS resulted in less (P = 0.03) DMI and ADG than SBM. From weeks 5 to 8, DDGS did not affect (P ≥ 0.23) DMI or ADG but resulted in a greater (P = 0.04) G:F than SBM. Final BW did not differ (P = 0.58) duo to protein source. Providing nisin had no impact on DMI (P = 0.44), ADG (P = 0.84), or G:F (P = 0.73). Nisin addition only affected plasma uric acid concentration (P = 0.04). It was concluded that DDGS could substitute for SBM as a nitrogen source to growing Hu lambs to reduce N excretion via urine without adverse effects on animal performance, but nisin supplementation probably had no additional benefits.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of sulfur and acidity on performance and digestibility in feedlot lambs fed dried distillers grains with solubles.J Anim Sci. 2013 May;91(5):2211-8. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5866. Epub 2013 Feb 13. J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 23408807 Clinical Trial.
-
Optimizing nitrogen utilization in growing steers fed forage diets supplemented with dried citrus pulp.J Anim Sci. 2007 Oct;85(10):2548-55. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0059. Epub 2007 May 25. J Anim Sci. 2007. PMID: 17526670
-
Effects of using ground redberry juniper and dried distillers grains with solubles in lamb feedlot diets: growth, blood serum, fecal, and wool characteristics.J Anim Sci. 2014 Mar;92(3):1119-32. doi: 10.2527/jas.2013-7007. Epub 2014 Feb 3. J Anim Sci. 2014. PMID: 24492543 Clinical Trial.
-
A dose-response meta-analysis of grape by-product effects on lamb growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and blood parameters.Animal. 2025 Mar;19(3):101449. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2025.101449. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Animal. 2025. PMID: 39978010
-
The influence of dietary fibre on protein digestion and utilization in monogastrics.Arch Tierernahr. 1995;48(1-2):89-95. doi: 10.1080/17450399509381831. Arch Tierernahr. 1995. PMID: 8526735 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative effects of nisin and monensin supplementation on growth performance, rumen fermentation, nutrient digestion, and plasma metabolites of fattening Hu sheep.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Aug 1;11:1441431. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1441431. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39149151 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary Nisin on growth performance, immune function, and gut health of broilers challenged by Clostridium perfringens.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 1;102:skae017. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae017. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38266070 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Dietary Protein Source and Level on Histological Properties of Muscle and Adipose Tissue of Lambs.Foods. 2023 Mar 17;12(6):1284. doi: 10.3390/foods12061284. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36981209 Free PMC article.
-
Soybean Oil, Linoleic Acid Source, in Lamb Diets: Intake, Digestibility, Performance, Ingestive Behaviour, and Blood Metabolites.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;14(14):2075. doi: 10.3390/ani14142075. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061537 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen Utilization and Ruminal Microbiota of Hu Lambs in Response to Varying Dietary Metabolizable Protein Levels.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 21;15(14):2147. doi: 10.3390/ani15142147. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson J. L., D. J. Schingoethe K. F. Kalscheur, and Hippen A. R.. 2006. Evaluation of dried and wet distillers grains included at two concentrations in the diets of lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 89:3133–3142. doi:10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(06)72587-5 - PubMed
-
- AOAC 1990. Official methods of analysis. 15th ed Arlington (VA): Association of Official Analytical Chemists.
-
- Avila-Stagno J., Chaves A. V., He M. L., and Mcallister T. A.. 2013. Increasing concentrations of wheat dry distillers’ grains with solubles in iso-nitrogenous finishing diets reduce lamb performance. Small Rumin. Res. 114:10–19. doi:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2013.05.003
-
- Barham D. and Trinder P.. 1972. An improved colour reagent for the determination of blood glucose by the oxidase system. Analyst 97:142–145. doi:10.1039/AN9729700142 - PubMed
-
- Benchaar C., F. Hassanat R. Gervais P. Y. Chouinard C. Julien H. V. Petit, and Massé D. I.. 2013. Effects of increasing amounts of corn dried distillers grains with solubles in dairy cow diets on methane production, ruminal fermentation, digestion, n balance, and milk production. j. Dairy Sci. 96:2413–2427. doi:10.3168/jds.2012-6037 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

