Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor positive breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- PMID: 29514654
- PMCID: PMC5842586
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-018-1332-7
Clinical significance and prognostic value of receptor conversion in hormone receptor positive breast cancers after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is widely used in advanced breast cancer patients. However, there is little known about conversion frequency of estrogen receptor (ER) and/or progesterone receptor (PR) status for hormone receptor positive-breast cancer patients after NAC and their correlation with prognosis.
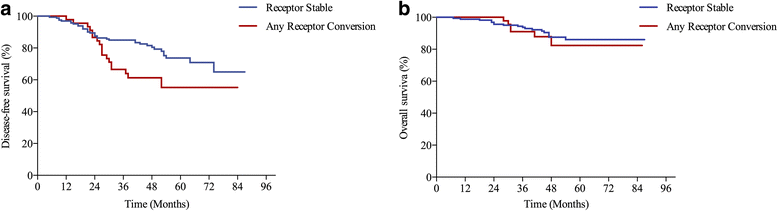
Methods: In this study, 231 breast cancer patients with residual disease after NAC were enrolled and divided into receptor stable group (having no conversion in both ER and PR status pre- and post-NAC) and any receptor conversion group (having any conversion in either ER or PR status). Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were used to compare survival differences between the two groups.
Results: Fifty-five patients (23.8%) had ER and/or PR conversion after NAC. Younger patients (≤ 50 years) were more likely to have receptor conversion (P = 0.014). For 213 patients (92.2%) who received adjuvant endocrinotherapy after surgery, the 5-year disease free survival (DFS) estimates for patients in the any receptor conversion group (55.2%) was worse than patients in the receptor stable group (73.7%, Log-rank test, P = 0.015). While the 5-year overall survival estimates for patients with or without receptor conversion were not statistically different (86.0 vs. 82.4%, Log-rank test, P = 0.587). In multivariate Cox proportional hazard analyses, patients with any receptor conversion had worse DFS (hazard ratio, 1.995; 95% confidence interval, 1.130-3.521, P = 0.031).
Conclusions: It is necessary to recommend patients to test biomarkers in residual disease and pay more attention to patients who have any receptor conversion. These patients may need more individual therapy after surgery.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Hormone receptor; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy; Receptor conversion.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the institutional Ethics Committee of the West China Hospital.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

