Effect of Mobile Phone Text Message Reminders on Routine Immunization Uptake in Pakistan: Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 29514773
- PMCID: PMC5863012
- DOI: 10.2196/publichealth.7026
Effect of Mobile Phone Text Message Reminders on Routine Immunization Uptake in Pakistan: Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Improved routine immunization (RI) coverage is recommended as the priority public health strategy to decrease vaccine-preventable diseases and eradicate polio in Pakistan and worldwide.
Objective: The objective of this study was to ascertain whether customized, automated, one-way text messaging (short message service, SMS) reminders delivered to caregivers via mobile phones when a child is due for an RI visit can improve vaccination uptake and timelines in Pakistan.
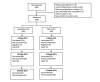
Methods: This was a randomized controlled trial, conducted in an urban squatter settlement area of Karachi, Pakistan. Infants less than 2 weeks of age with at least one family member who had a valid mobile phone connection and was comfortable receiving and reading SMS text messages were included. Participants were randomized to the intervention (standard care + one-way SMS reminder) or control (standard care) groups. The primary outcome was to compare the proportion of children immunized up to date at 18 weeks of age. Vaccine given at 6, 10, and 14 weeks schedule includes DPT-Hep-B-Hib vaccine (ie, diphtheria, pertussis, and tetanus; hepatitis B; and Haemophilus influenza type b) and oral poliovirus vaccine (OPV). Data were analyzed using chi-square tests of independence and tested for both per protocol (PP) and intention-to-treat (ITT) analyses.
Results: Out of those approached, 84.3% (300/356) of the participants were eligible for enrollment and 94.1% (318/338) of the participants had a working mobile phone. Only children in the PP analyses, who received an SMS reminder for vaccine uptake at 6 weeks visit, showed a statistically significant difference (96.0%, 86/90 vs 86.4%, 102/118; P=.03).The immunization coverage was consistently higher in the intervention group according to ITT analyses at the 6 weeks scheduled visit (76.0% vs 71.3%, P=.36). The 10 weeks scheduled visit (58.7% vs 52.7%, P=.30) and the 14 weeks scheduled visit (31.3% vs 26.0%, P=.31), however, were not statistically significant.
Conclusions: Automated simple one-way SMS reminders in local languages might be feasible for improving routine vaccination coverage. Whether one-way SMS reminders alone can have a strong impact on parental attitudes and behavior for improvement of RI coverage and timeliness needs to be further evaluated by better-powered studies and by comparing different types and content of text messages in low-and middle-income countries (LMICs).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01859546; https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01859546 (Archived by WebCite at http://www.webcitation.org/6xFr57AOc).
Keywords: SMS; children; low- and middle-income countries; mobile phone; reminders; routine immunization.
©Abdul Momin Kazi, Murtaza Ali, Khurram Zubair, Hussain Kalimuddin, Abdul Nafey Kazi, Saleem Perwaiz Iqbal, Jean-Paul Collet, Syed Asad Ali. Originally published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance (http://publichealth.jmir.org), 07.03.2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Miller M, Hinman A. Vaccines. 4th ed. Philadelphia: PAlsevier Inc; 2004. Chapter 57: Economic analyses of vaccine policies.
-
- World Health Organization. 2016. [2016-11-17]. Immunization coverage Internet http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs378/en/ 6m6WZZ9IT
-
- Owais A, Hanif B, Siddiqui AR, Agha A, Zaidi AK. Does improving maternal knowledge of vaccines impact infant immunization rates? A community-based randomized-controlled trial in Karachi, Pakistan. BMC Public Health. 2011 Apr 17;11:239. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-239. https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2458-11-239 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kalan R, Wiysonge CS, Ramafuthole T, Allie K, Ebrahim F, Engel ME. Mobile phone text messaging for improving the uptake of vaccinations: a systematic review protocol. BMJ Open. 2014 Aug 04;4(8):e005130. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005130. http://bmjopen.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=25091013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shen AK, Fields R, McQuestion M. The future of routine immunization in the developing world: challenges and opportunities. Glob Health Sci Pract. 2014 Dec 10;2(4):381–94. doi: 10.9745/GHSP-D-14-00137. http://www.ghspjournal.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=25611473 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

