Association of Atrial Fibrillation With Cognitive Decline and Dementia Over 20 Years: The ARIC-NCS (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Neurocognitive Study)
- PMID: 29514809
- PMCID: PMC5907543
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007301
Association of Atrial Fibrillation With Cognitive Decline and Dementia Over 20 Years: The ARIC-NCS (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Neurocognitive Study)
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have reported that atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with cognitive decline and dementia. These studies, however, had limited follow-up, were based mostly on white and highly selected populations, and did not account for attrition. We evaluated the association of incident AF with 20-year change in cognitive performance (accounting for attrition) and incident dementia in the ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) Study.
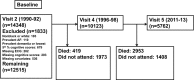
Methods and results: We analyzed data from 12 515 participants (mean age, 56.9 [SD, 5.7] years in 1990-1992; 56% women and 24% black) from 1990 to 1992 through 2011 to 2013. Incident AF was ascertained from study ECGs and hospital discharge codes. Cognitive tests were performed in 1990 to 1992, 1996 to 1998, and 2011 to 2013. Incident dementia was clinician adjudicated. We used generalized estimating equations and Cox proportional hazards models to assess the association of time-dependent AF with change in Z scores of cognitive tests and incident dementia, respectively. During 20 years, 2106 participants developed AF and 1157 participants developed dementia. After accounting for cardiovascular risk factors, including ischemic stroke, the average decline over 20 years in global cognitive Z score was 0.115 (95% confidence interval, 0.014-0.215) greater in participants with AF than in those without AF. Further adjustment for attrition by multiple imputation by chained equations strengthened the association. In addition, incident AF was associated with an increased risk of dementia (hazard ratio, 1.23; 95% confidence interval, 1.04-1.45), after adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors, including ischemic stroke.
Conclusions: AF is associated with greater cognitive decline and increased risk of dementia, independent of ischemic stroke. Because cognitive decline is a precursor to dementia, our findings prompt further investigation to identify specific treatments for AF that will delay the trajectory of cognitive decline and, thus, prevent dementia in patients with AF.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; cognition; cohort study; dementia; epidemiology.
© 2018 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures
References
-
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, Singer DE. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–2375. - PubMed
-
- Miyasaka Y, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Cha SS, Bailey KR, Abhayaratna WP, Seward JB, Tsang TSM. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation. 2006;114:119–125. - PubMed
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22:983–988. PMID:1866765. - PubMed
-
- Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, Leip EP, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Murabito JM, Kannel WB, Benjamin EJ. Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure and their joint influence on mortality: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2003;107:2920–2925. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998;98:946–952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 16EIA26410001/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- U01 HL096902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL126637/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG052573/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical