Physiological Regulation of Drug Metabolism and Transport: Pregnancy, Microbiome, Inflammation, Infection, and Fasting
- PMID: 29514828
- PMCID: PMC5885931
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.117.079905
Physiological Regulation of Drug Metabolism and Transport: Pregnancy, Microbiome, Inflammation, Infection, and Fasting
Abstract
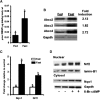
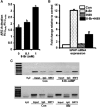
This article is a report on a symposium entitled "Physiological Regulation of Drug Metabolism and Transport" sponsored by the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and held at the Experimental Biology 2017 meeting in Chicago, IL. The contributions of physiologic and pathophysiological regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters to interindividual variability in drug metabolism are increasingly recognized but in many cases are not well understood. The presentations herein discuss the phenomenology, consequences, and mechanism of such regulation. CYP2D6 transgenic mice were used to provide insights into the mechanism of regulation of this enzyme in pregnancy, via hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α, small heterodimer partner, and retinoids. Regulation of intestinal and hepatic drug-processing enzymes by the intestinal microbiota via tryptophan and its metabolites was investigated. The potential impact of parasitic infections on human drug metabolism and clearance was assessed in mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni or Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi AS, both of which produced widespread and profound effects on murine hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes. Finally, the induction of Abcc drug efflux transporters by fasting was investigated. This was demonstrated to occur via a cAMP, protein kinase A/nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2/Sirtuin 1 pathway via antioxidant response elements on the Abcc genes.
Copyright © 2018 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures




References
-
- Aitken AE, Richardson TA, Morgan ET. (2006) Regulation of drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters in inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 46:123–149. - PubMed
-
- Akinyinka OO, Sowunmi A, Honeywell R, Renwick AG. (2000a) The effects of acute falciparum malaria on the disposition of caffeine and the comparison of saliva and plasma-derived pharmacokinetic parameters in adult Nigerians. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56:159–165. - PubMed
-
- Akinyinka OO, Sowunmi A, Honeywell R, Renwick AG. (2000b) The pharmacokinetics of caffeine in Nigerian children suffering from malaria and kwashiorkor. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56:153–158. - PubMed
-
- Babalola CP, Bolaji OO, Ogunbona FA, Sowunmi A, Walker O. (1998) Pharmacokinetics of quinine in African patients with acute falciparum malaria. Pharm World Sci 20:118–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

