Dynamics of Tissue-Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses during West Nile Virus Infection
- PMID: 29514902
- PMCID: PMC5923067
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00014-18
Dynamics of Tissue-Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses during West Nile Virus Infection
Abstract
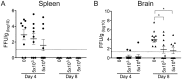
The mouse model of West Nile virus (WNV), which is a leading cause of mosquito-borne encephalitis worldwide, has provided fundamental insights into the host and viral factors that regulate viral pathogenesis and infection outcome. In particular, CD8+ T cells are critical for controlling WNV replication and promoting protection against infection. Here, we present the characterization of a T cell receptor (TCR)-transgenic mouse with specificity for the immunodominant epitope in the WNV NS4B protein (here referred to as transgenic WNV-I mice). Using an adoptive-transfer model, we found that WNV-I CD8+ T cells behave similarly to endogenous CD8+ T cell responses, with an expansion phase in the periphery beginning around day 7 postinfection (p.i.) followed by a contraction phase through day 15 p.i. Through the use of in vivo intravascular immune cell staining, we determined the kinetics, expansion, and differentiation into effector and memory subsets of WNV-I CD8+ T cells within the spleen and brain. We found that red-pulp WNV-I CD8+ T cells were more effector-like than white-pulp WNV-I CD8+ T cells, which displayed increased differentiation into memory precursor cells. Within the central nervous system (CNS), we found that WNV-I CD8+ T cells were polyfunctional (gamma interferon [IFN-γ] and tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]), displayed tissue-resident characteristics (CD69+ and CD103+), persisted in the brain through day 15 p.i., and reduced the viral burden within the brain. The use of these TCR-transgenic WNV-I mice provides a new resource to dissect the immunological mechanisms of CD8+ T cell-mediated protection during WNV infection.IMPORTANCE West Nile Virus (WNV) is the leading cause of mosquito-borne encephalitis worldwide. There are currently no approved therapeutics or vaccines for use in humans to treat or prevent WNV infection. CD8+ T cells are critical for controlling WNV replication and protecting against infection. Here, we present a comprehensive characterization of a novel TCR-transgenic mouse with specificity for the immunodominant epitope in the WNV NS4B protein. In this study, we determine the kinetics, proliferation, differentiation into effector and memory subsets, homing, and clearance of WNV in the CNS. Our findings provide a new resource to dissect the immunological mechanisms of CD8+ T cell-mediated protection during WNV infection.
Keywords: CD8+ T cells; West Nile virus; brain; neuroimmunology; spleen; viral pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Mostashari F, Bunning ML, Kitsutani PT, Singer DA, Nash D, Cooper MJ, Katz N, Liljebjelke KA, Biggerstaff BJ, Fine AD, Layton MC, Mullin SM, Johnson AJ, Martin DA, Hayes EB, Campbell GL. 2001. Epidemic West Nile encephalitis, New York, 1999: results of a household-based seroepidemiological survey. Lancet 358:261–264. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05480-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murray K, Baraniuk S, Resnick M, Arafat R, Kilborn C, Cain K, Shallenberger R, York TL, Martinez D, Hellums JS, Hellums D, Malkoff M, Elgawley N, McNeely W, Khuwaja SA, Tesh RB. 2006. Risk factors for encephalitis and death from West Nile virus infection. Epidemiol Infect 134:1325–1332. doi: 10.1017/S0950268806006339. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

