Adenovirus Vector Vaccination Impacts NK Cell Rheostat Function following Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection
- PMID: 29514912
- PMCID: PMC5952142
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02103-17
Adenovirus Vector Vaccination Impacts NK Cell Rheostat Function following Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus Infection
Abstract
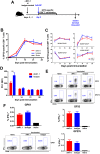
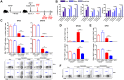
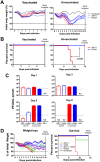
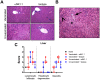
Natural killer (NK) cells respond rapidly as a first line of defense against infectious pathogens. In addition, NK cells may provide a "rheostat" function and have been shown to reduce the magnitude of antigen-specific T cell responses following infection to avoid immunopathology. However, it remains unknown whether NK cells similarly modulate vaccine-elicited T cell responses following virus challenge. We used the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) clone 13 infection model to address whether NK cells regulate T cell responses in adenovirus vector-vaccinated mice following challenge. As expected, NK cell depletion in unvaccinated mice resulted in increased virus-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses and immunopathology following LCMV challenge. In contrast, NK cell depletion had minimal to no impact on antigen-specific T cell responses in mice that were vaccinated with an adenovirus serotype 5 (Ad5)-GP vector prior to LCMV challenge. Moreover, NK cell depletion in vaccinated mice prior to challenge did not result in immunopathology and did not compromise protective efficacy. These data suggest that adenovirus vaccine-elicited T cells may be less sensitive to NK cell rheostat regulation than T cells primed by LCMV infection.IMPORTANCE Recent data have shown that NK cell depletion leads to enhanced virus-elicited T cell responses that can result in severe immunopathology following LCMV infection in mice. In this study, we observed that NK cells exerted minimal to no impact on vaccine-elicited T cells following LCMV challenge, suggesting that adenovirus vaccine-elicited T cells may be less subject to NK cell regulation. These data contribute to our understanding of NK cell regulatory functions and T cell-based vaccines.
Keywords: NK cells; adenoviruses; lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus; vaccines.
Copyright © 2018 Blass et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vaccination against lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection in MHC class II-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2011 Apr 1;186(7):3997-4007. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001251. Epub 2011 Feb 28. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21357263
-
Adenovirus Serotype 5 Vaccination Results in Suboptimal CD4 T Helper 1 Responses in Mice.J Virol. 2017 Feb 14;91(5):e01132-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01132-16. Print 2017 Mar 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28003483 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of adenovirus type 5 vector-induced memory CD8 T cells: not as bad as their reputation.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(11):6283-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00465-13. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23536658 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic LCMV Infection Is Fortified with Versatile Tactics to Suppress Host T Cell Immunity and Establish Viral Persistence.Viruses. 2021 Sep 29;13(10):1951. doi: 10.3390/v13101951. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis infection of the central nervous system.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:4529-43. doi: 10.2741/3021. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dichotomous Regulation of Acquired Immunity by Innate Lymphoid Cells.Cells. 2020 May 11;9(5):1193. doi: 10.3390/cells9051193. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32403291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutually assured destruction: the cold war between viruses and natural killer cells.Curr Opin Virol. 2019 Feb;34:130-139. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Curr Opin Virol. 2019. PMID: 30877885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cell immunosuppressive function requires CXCR3-dependent redistribution within lymphoid tissues.J Clin Invest. 2021 Sep 15;131(18):e146686. doi: 10.1172/JCI146686. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 34314390 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting natural killer cells to enhance vaccine responses.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Sep;42(9):789-801. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34311992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germline natural killer cell receptors modulating the T cell response.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 4;15:1477991. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1477991. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39559364 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

