CB1R-Mediated Activation of Caspase-3 Causes Epigenetic and Neurobehavioral Abnormalities in Postnatal Ethanol-Exposed Mice
- PMID: 29515368
- PMCID: PMC5826222
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00045
CB1R-Mediated Activation of Caspase-3 Causes Epigenetic and Neurobehavioral Abnormalities in Postnatal Ethanol-Exposed Mice
Abstract
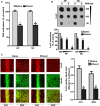
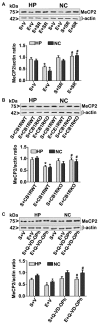
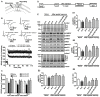
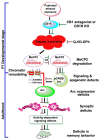
Alcohol exposure can affect brain development, leading to long-lasting behavioral problems, including cognitive impairment, which together is defined as fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD). However, the fundamental mechanisms through which this occurs are largely unknown. In this study, we report that the exposure of postnatal day 7 (P7) mice to ethanol activates caspase-3 via cannabinoid receptor type-1 (CB1R) in neonatal mice and causes a reduction in methylated DNA binding protein (MeCP2) levels. The developmental expression of MeCP2 in mice is closely correlated with synaptogenesis and neuronal maturation. It was shown that ethanol treatment of P7 mice enhanced Mecp2 mRNA levels but reduced protein levels. The genetic deletion of CB1R prevented, and administration of a CB1R antagonist before ethanol treatment of P7 mice inhibited caspase-3 activation. Additionally, it reversed the loss of MeCP2 protein, cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) activation, and activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (Arc) expression. The inhibition of caspase-3 activity prior to ethanol administration prevented ethanol-induced loss of MeCP2, CREB activation, epigenetic regulation of Arc expression, long-term potentiation (LTP), spatial memory deficits and activity-dependent impairment of several signaling molecules, including MeCP2, in adult mice. Collectively, these results reveal that the ethanol-induced CB1R-mediated activation of caspase-3 degrades the MeCP2 protein in the P7 mouse brain and causes long-lasting neurobehavioral deficits in adult mice. This CB1R-mediated instability of MeCP2 during active synaptic maturation may disrupt synaptic circuit maturation and lead to neurobehavioral abnormalities, as observed in this animal model of FASD.
Keywords: DNA methylation; FASD; MeCP2; neurodegeneration; synaptic plasticity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
CB1R regulates CDK5 signaling and epigenetically controls Rac1 expression contributing to neurobehavioral abnormalities in mice postnatally exposed to ethanol.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019 Feb;44(3):514-525. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0181-y. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30143782 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol exposure induces neonatal neurodegeneration by enhancing CB1R Exon1 histone H4K8 acetylation and up-regulating CB1R function causing neurobehavioral abnormalities in adult mice.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Oct 31;18(5):pyu028. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu028. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25609594 Free PMC article.
-
CB1-receptor knockout neonatal mice are protected against ethanol-induced impairments of DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNA methylation.J Neurochem. 2015 Feb;132(4):429-442. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13006. Epub 2015 Jan 27. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25487288 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Developmental Alcohol-Induced Neurobehavioral Deficits.Brain Sci. 2016 Apr 8;6(2):12. doi: 10.3390/brainsci6020012. Brain Sci. 2016. PMID: 27070644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shaping synaptic plasticity: the role of activity-mediated epigenetic regulation on gene transcription.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 Oct;31(6):359-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 9. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23665156 Review.
Cited by
-
Binge-like Prenatal Ethanol Exposure Causes Impaired Cellular Differentiation in the Embryonic Forebrain and Synaptic and Behavioral Defects in Adult Mice.Brain Sci. 2022 Jun 17;12(6):793. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12060793. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35741678 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal Ethanol Exposure Activates HDAC-Mediated Histone Deacetylation, Impairs Synaptic Plasticity Gene Expression and Behavior in Mice.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 May 27;23(5):324-338. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa017. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32170298 Free PMC article.
-
Anastasis confers ovarian cancer cells increased malignancy through elevated p38 MAPK activation.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Mar;30(3):809-824. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01081-1. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 36447048 Free PMC article.
-
Endocannabinoid signaling and epigenetics modifications in the neurobiology of stress-related disorders.Neuronal Signal. 2023 Jul 25;7(2):NS20220034. doi: 10.1042/NS20220034. eCollection 2023 Jul. Neuronal Signal. 2023. PMID: 37520658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomic and Other Evidence for Cannabis-Induced Aging Contextualized in a Synthetic Epidemiologic Overview of Cannabinoid-Related Teratogenesis and Cannabinoid-Related Carcinogenesis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 13;19(24):16721. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416721. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36554603 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abel E. L., Jacobson S., Sherwin B. T. (1983). In utero alcohol exposure: functional and structural brain damage. Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol. 5, 363–366. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

