IGF Binding Protein-5 Induces Cell Senescence
- PMID: 29515523
- PMCID: PMC5826077
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00053
IGF Binding Protein-5 Induces Cell Senescence
Abstract
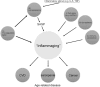
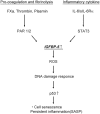
Cellular senescence is the complex process of deterioration that drives the aging of an organism, resulting in the progressive loss of organ function and eventually phenotypic aging. Senescent cells undergo irreversible growth arrest, usually by inducing telomere shortening. Alternatively, senescence may also occur prematurely in response to various stress stimuli, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, or activated oncogenes. Recently, it has been shown that IGF binding protein-5 (IGFBP-5) with the induction of the tumor suppressor p53 is upregulated during cellular senescence. This mechanism mediates interleukin-6/gp130-induced premature senescence in human fibroblasts, irradiation-induced premature senescence in human endothelial cells (ECs), and replicative senescence in human ECs independent of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-II. Additionally, a link between IGFBP-5, hyper-coagulation, and inflammation, which occur with age, has been implicated. Thus, IGFBP-5 seems to play decisive roles in controlling cell senescence and cell inflammation. In this review, we describe the accumulating evidence for this role of IGFBP-5 including our new finding.
Keywords: IGF binding protein-5; age-related disease; cell senescence; coagulation system; inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of cellular senescence by insulin-like growth factor binding protein-5 through a p53-dependent mechanism.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Nov;18(11):4543-52. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-03-0280. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17804819 Free PMC article.
-
Irreversible cellular senescence induced by prolonged exposure to H2O2 involves DNA-damage-and-repair genes and telomere shortening.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;37(7):1407-20. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.01.010. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15833273
-
Stress-induced premature senescence or stress-induced senescence-like phenotype: one in vivo reality, two possible definitions?ScientificWorldJournal. 2002 Jan 29;2:230-47. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2002.100. ScientificWorldJournal. 2002. PMID: 12806055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquisition of oxidative DNA damage during senescence: the first step toward carcinogenesis?Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1119:51-63. doi: 10.1196/annals.1404.010. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 18056954 Review.
-
Critical telomere shortening regulated by the ataxia-telangiectasia gene acts as a DNA damage signal leading to activation of p53 protein and limited life-span of human diploid fibroblasts. A review.Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997 Nov;62(11):1306-10. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997. PMID: 9467855 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma proteome profiling of healthy individuals across the life span in a Sicilian cohort with long-lived individuals.Aging Cell. 2022 Sep;21(9):e13684. doi: 10.1111/acel.13684. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Aging Cell. 2022. PMID: 35932462 Free PMC article.
-
IGFBP5 Promotes Neuronal Apoptosis in a 6-OHDA-Toxicant Model of Parkinson's Disease by Inhibiting the Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway.Med Princ Pract. 2024;33(3):269-280. doi: 10.1159/000538467. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Med Princ Pract. 2024. PMID: 38565090 Free PMC article.
-
STMN1-IGFBP5 axis induces senescence and extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cells: In vivo and in vitro insights.Mol Med. 2025 May 3;31(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01220-7. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40319242 Free PMC article.
-
A Pro-Regenerative Environment Triggers Premalignant to Malignant Transformation of Senescent Hepatocytes.Cancer Res. 2023 Feb 3;83(3):428-440. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-1477. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36449018 Free PMC article.
-
Sorafenib, rapamycin, and venetoclax attenuate doxorubicin-induced senescence and promote apoptosis in HCT116 cells.Saudi Pharm J. 2022 Jan;30(1):91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.12.004. Epub 2021 Dec 31. Saudi Pharm J. 2022. PMID: 35145348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li P, Sun X, Cai G, Chen X. Insulin-like growth factor system and aging. J Aging Sci (2017) 5:171.10.4172/2329-8847.1000171 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

