Recovering Genomics Clusters of Secondary Metabolites from Lakes Using Genome-Resolved Metagenomics
- PMID: 29515540
- PMCID: PMC5826242
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00251
Recovering Genomics Clusters of Secondary Metabolites from Lakes Using Genome-Resolved Metagenomics
Abstract
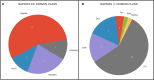
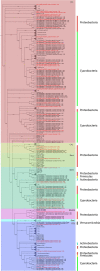
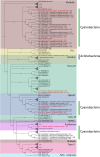
Metagenomic approaches became increasingly popular in the past decades due to decreasing costs of DNA sequencing and bioinformatics development. So far, however, the recovery of long genes coding for secondary metabolites still represents a big challenge. Often, the quality of metagenome assemblies is poor, especially in environments with a high microbial diversity where sequence coverage is low and complexity of natural communities high. Recently, new and improved algorithms for binning environmental reads and contigs have been developed to overcome such limitations. Some of these algorithms use a similarity detection approach to classify the obtained reads into taxonomical units and to assemble draft genomes. This approach, however, is quite limited since it can classify exclusively sequences similar to those available (and well classified) in the databases. In this work, we used draft genomes from Lake Stechlin, north-eastern Germany, recovered by MetaBat, an efficient binning tool that integrates empirical probabilistic distances of genome abundance, and tetranucleotide frequency for accurate metagenome binning. These genomes were screened for secondary metabolism genes, such as polyketide synthases (PKS) and non-ribosomal peptide synthases (NRPS), using the Anti-SMASH and NAPDOS workflows. With this approach we were able to identify 243 secondary metabolite clusters from 121 genomes recovered from our lake samples. A total of 18 NRPS, 19 PKS, and 3 hybrid PKS/NRPS clusters were found. In addition, it was possible to predict the partial structure of several secondary metabolite clusters allowing for taxonomical classifications and phylogenetic inferences. Our approach revealed a high potential to recover and study secondary metabolites genes from any aquatic ecosystem.
Keywords: NRPS; PKS; environmental genomics; freshwater; metagenomics 2.0.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reconstructing Draft Genomes Using Genome Resolved Metagenomics Reveal Arsenic Metabolizing Genes and Secondary Metabolites in Fresh Water Lake in Eastern India.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2021 Jun 22;15:11779322211025332. doi: 10.1177/11779322211025332. eCollection 2021. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2021. PMID: 34220198 Free PMC article.
-
Epilithic Biofilms in Lake Baikal: Screening and Diversity of PKS and NRPS Genes in the Genomes of Heterotrophic Bacteria.Pol J Microbiol. 2018;67(4):501-516. doi: 10.21307/pjm-2018-060. Pol J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30550237 Free PMC article.
-
The natural product domain seeker NaPDoS: a phylogeny based bioinformatic tool to classify secondary metabolite gene diversity.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034064. Epub 2012 Mar 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479523 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive compounds synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases and type-I polyketide synthases discovered through genome-mining and metagenomics.Biotechnol Lett. 2012 Aug;34(8):1393-403. doi: 10.1007/s10529-012-0919-2. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Biotechnol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22481301 Review.
-
Discovery Strategies of Bioactive Compounds Synthesized by Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases and Type-I Polyketide Synthases Derived from Marine Microbiomes.Mar Drugs. 2016 Apr 16;14(4):80. doi: 10.3390/md14040080. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27092515 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthetic gene clusters from uncultivated soil bacteria of the Atacama Desert.mSphere. 2024 Oct 29;9(10):e0019224. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00192-24. Epub 2024 Sep 17. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39287428 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Newer Biosynthetic Gene Clusters in Marine Microbial Prospecting.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022 Jun;24(3):448-467. doi: 10.1007/s10126-022-10118-y. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2022. PMID: 35394575 Review.
-
Discovery of an Abundance of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters in Shark Bay Microbial Mats.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1950. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01950. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32973707 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of Genomic Information in Multiple Displacement Amplified Low-Quantity Metagenomic Material from Marine Invertebrates.Mar Drugs. 2023 Mar 2;21(3):165. doi: 10.3390/md21030165. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36976214 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of Polyketide Synthases and Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases Revealed Through Metagenomic Analysis of a Deep Oligotrophic Cave.Microb Ecol. 2021 Jan;81(1):110-121. doi: 10.1007/s00248-020-01554-1. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Microb Ecol. 2021. PMID: 32638044
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

