Enterovirus A71 Proteins: Structure and Function
- PMID: 29515559
- PMCID: PMC5826392
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00286
Enterovirus A71 Proteins: Structure and Function
Abstract
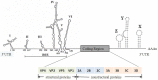
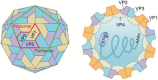
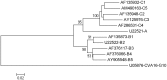
Enterovirus A71 (EV-A71) infection has grown to become a serious threat to global public health. It is one of the major causes of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) in infants and young children. EV-A71 can also infect the central nervous system (CNS) and induce diverse neurological complications, such as brainstem encephalitis, aseptic meningitis, and acute flaccid paralysis, or even death. Viral proteins play a crucial role in EV-A71 infection. Many recent studies have discussed the structure and function of EV-A71 proteins, and the findings reported will definitely aid the development of vaccines and therapeutic approaches. This article reviews the progress in the research on the structure and function of EV-A71 proteins. Available literature can provide a basis for studying the pathogenesis of EV-A71 infection in detail.
Keywords: enterovirus-A71; epitope; function; protein; structure.
Figures
References
-
- Chan L. G., Parashar U. D., Lye M. S., Ong F. G., Zaki S. R., Alexander J. P., et al. . (2000). Deaths of children during an outbreak of hand, foot, and mouth disease in sarawak, malaysia: clinical and pathological characteristics of the disease. for the outbreak study group. Clin. Infect. Dis. 31, 678–683. 10.1086/314032 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

