Therapeutic target discovery using Boolean network attractors: improvements of kali
- PMID: 29515890
- PMCID: PMC5830779
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.171852
Therapeutic target discovery using Boolean network attractors: improvements of kali
Abstract
In a previous article, an algorithm for identifying therapeutic targets in Boolean networks modelling pathological mechanisms was introduced. In the present article, the improvements made on this algorithm, named kali, are described. These improvements are (i) the possibility to work on asynchronous Boolean networks, (ii) a finer assessment of therapeutic targets and (iii) the possibility to use multivalued logic. kali assumes that the attractors of a dynamical system, such as a Boolean network, are associated with the phenotypes of the modelled biological system. Given a logic-based model of pathological mechanisms, kali searches for therapeutic targets able to reduce the reachability of the attractors associated with pathological phenotypes, thus reducing their likeliness. kali is illustrated on an example network and used on a biological case study. The case study is a published logic-based model of bladder tumorigenesis from which kali returns consistent results. However, like any computational tool, kali can predict but cannot replace human expertise: it is a supporting tool for coping with the complexity of biological systems in the field of drug discovery.
Keywords: Boolean network; attractor; biological network; bladder cancer; drug discovery; therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
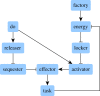
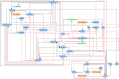
References
-
- Poret A, Boissel J-P. 2014. An in silico target identification using Boolean network attractors: avoiding pathological phenotypes. C. R. Biol. 337, 661–678. (doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2014.10.002) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Le Novere N. 2015. Quantitative and logic modelling of molecular and gene networks. Nat. Rev. Genet. 16, 146–158. (doi:10.1038/nrg3885) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wynn ML, Consul N, Merajver SD, Schnell S. 2012. Logic-based models in systems biology: a predictive and parameter-free network analysis method. Integr. Biol. (Camb) 4, 1323–1337. (doi:10.1039/c2ib20193c) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morris MK, Saez-Rodriguez J, Sorger PK, Lauffenburger DA. 2010. Logic-based models for the analysis of cell signaling networks. Biochemistry 49, 3216–3224. (doi:10.1021/bi902202q) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albert R, Thakar J. 2014. Boolean modeling: a logic-based dynamic approach for understanding signaling and regulatory networks and for making useful predictions. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Syst. Biol. Med. 6, 353–369. (doi:10.1002/wsbm.1273) - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
