Neurocognitive impairment with hepatitis C and HIV co-infection in Southern Brazil
- PMID: 29516346
- PMCID: PMC5993600
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-018-0617-5
Neurocognitive impairment with hepatitis C and HIV co-infection in Southern Brazil
Abstract
Although cognitive impairment has been well documented in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) mono-infections, research on neurocognitive effects is limited in the context of HIV/HCV co-infection. The aims of this study were to explore the interplay between HIV and HCV infections in the expression of neurocognitive impairment (NCI), and to examine the differences in test performance between HIV/HCV co-infected and HIV or HCV mono-infected patients. A total of 128 participants from Southern Brazil underwent a comprehensive neuropsychological (NP) battery comprising 18 tests. Participants were grouped according to their serological status: HCV mono-infected (n = 20), HIV mono-infected (n = 48), HIV/HCV co-infected (n = 12), and HIV-/HCV-uninfected controls (n = 48). The frequencies of HIV subtypes B and C between the HIV mono-infected and HIV/HCV co-infected groups were comparable. There was greater prevalence of neuropsychological impairment among all three infection groups compared with the uninfected control group, but no statistically significant differences among mono- and co-infected groups were found. HCV infection was associated with cognitive deficits, independently of liver dysfunction. HCV infection did not show an additive effect on neurocognitive function among HIV+. NCI was independent of HCV RNA on peripheral blood, CSF, and hepatic injury. While we did not find additive global effect, in the present study, there was some evidence of additive HIV/HCV co-infection effects in speed of information processing, executive function, and verbal fluency domains when comparing the co-infected group with the other three groups. NP impairment was not dependent on HCV subtypes.
Keywords: HCV; HIV-1; HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND).
Conflict of interest statement
Sérgio Monteiro de Almeida, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Ana Paula de Pereira, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Maria Lucia Alves Pedroso, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Clea E. Ribeiro, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Indianara Rotta, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Bin Tang, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Anya Umlauf, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Donald Franklin, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Rowan G Saloner, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Maria Geny Ribas Batista, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Scott Letendre, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Robert K. Heaton, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Ronald J. Ellis, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Mariana Cherner, the author declare that have no conflict of interest.
Figures
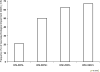
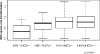
References
-
- Brasil, Ministério da Saúde. Programa Nacional de DST/AIDS. 2016 http://www.aids.gov.br/assistencia/manualdst/item12.htm.
-
- Cacciarelli TV, Martinez OM, Gish RG, Villanueva JC, Krams SM. Immunoregulatory cytokines in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: Pre- and posttreatment with interferon alfa. Hepatology. 1996;24:6–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

