Use and effectiveness of dapagliflozin in routine clinical practice: An Italian multicentre retrospective study
- PMID: 29516612
- PMCID: PMC6175069
- DOI: 10.1111/dom.13280
Use and effectiveness of dapagliflozin in routine clinical practice: An Italian multicentre retrospective study
Abstract
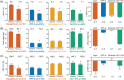
In randomized controlled trials (RCTs), sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have been shown to confer glycaemic and extra-glycaemic benefits. The DARWIN-T2D (DApagliflozin Real World evIdeNce in Type 2 Diabetes) study was a multicentre retrospective study designed to evaluate the baseline characteristics of patients receiving dapagliflozin vs those receiving selected comparators (dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, gliclazide, or glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists), and drug effectiveness in routine clinical practice. From a population of 281 217, the analysis included 17 285 patients initiating dapagliflozin or comparator glucose-lowering medications (GLMs), 6751 of whom had a follow-up examination. At baseline, participants starting dapagliflozin were younger, had a longer disease duration, higher glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) concentration, and a more complex history of previous GLM use, but the clinical profile of patients receiving dapagliflozin changed during the study period. Dapagliflozin reduced HbA1c by 0.7%, body weight by 2.7 kg, and systolic blood pressure by 3.0 mm Hg. Effects of comparator GLMs were also within the expected range, based on RCTs. This real-world study shows an initial channelling of dapagliflozin to difficult-to-treat patients. Nonetheless, dapagliflozin provided significant benefits with regard to glucose control, body weight and blood pressure that were in line with findings from RCTs.
Keywords: cohort study; dapagliflozin; glycaemic control; observational study; type 2 diabetes; weight control.
© 2018 The Authors. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
G.P.F. has received grant support, lecture or advisory board fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, NovoNordisk, Sanofi, Genzyme, Abbott, Novartis and Merck Sharp & Dohme.
A.C. has received consultancy or speaker fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Bruno Farmaceutici, Janssen, Eli‐Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, NovoNordisk, Roche, Sanofi‐Aventis, Servier and Takeda. He has also received research grants from Eli‐Lilly and NovoNordisk. A.G. has received consultancy or speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Eli‐Lilly, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Sanofi‐Aventis and Takeda. He has also received a research grant from AstraZeneca. G.S. has received fees for advisory work or lectures from Servier, Intarcia Therapeutics Inc, NovoNordisk, Janssen, Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme Italy, Lilly, Sanofi, Novartis, Abbott and Takeda. A.A. has received research grants, lecture or advisory board fees from Merck Sharp & Dome, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Boeringher‐Ingelheim, Sanofi, Mediolanum, Janssen, NovoNordisk, Lilly, Servier and Takeda. G.Z., D.B. and I.B. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdul‐Ghani MA, Norton L, Defronzo RA. Role of sodium‐glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT 2) inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev. 2011;32:515‐531. - PubMed
-
- Baker WL, Smyth LR, Riche DM, Bourret EM, Chamberlin KW, White WB. Effects of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter 2 inhibitors on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8:262‐275, e269. - PubMed
-
- Monami M, Nardini C, Mannucci E. Efficacy and safety of sodium glucose co‐transport‐2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a meta‐analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014;16:457‐466. - PubMed
-
- Frieden TR. Evidence for health decision making ‐ beyond randomized, controlled trials. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:465‐475. - PubMed
-
- Patel A, Billot L. Reality and truth. Balancing the hope and the hype of real‐world evidence. Circulation. 2017;136:260‐262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

