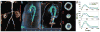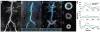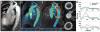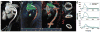Volumetric segmentation-free method for rapid visualization of vascular wall shear stress using 4D flow MRI
- PMID: 29516632
- PMCID: PMC5910222
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27159
Volumetric segmentation-free method for rapid visualization of vascular wall shear stress using 4D flow MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a rapid segmentation-free method to visualize and compute wall shear stress (WSS) throughout the aorta using 4D Flow MRI data. WSS is the drag force-per-area the vessel endothelium exerts on luminal blood; abnormal levels of WSS are associated with cardiovascular pathologies. Previous methods for computing WSS are bottlenecked by labor-intensive manual segmentation of vessel boundaries. A rapid automated segmentation-free method for computing WSS is presented.
Theory and methods: Shear stress is the dot-product of the viscous stress tensor and the inward normal vector. The inward normal vectors are approximated as the gradient of fluid speed at every voxel. Subsequently, a 4D map of shear stress is computed as the partial derivatives of velocity with respect to the inward normal vectors. We highlight the shear stress near the wall by fusing visualization with edge-emphasized anatomical data.
Results: As a proof-of-concept, four cases with aortic pathologies are presented. Visualization allows for rapid localization of pathologic WSS. Subsequent analysis of these pathological regions enables quantification of WSS. Average WSS during peak systole measures approximately 50-60 cPa in nonpathological regions of the aorta and is elevated in regions of stenosis, coarctation, and dissection. WSS is reduced in regions of aneurysm.
Conclusion: A volumetric technique for calculation and visualization of WSS from 4D Flow MRI data is presented. Traditional labor-intensive methods for WSS rely on explicit manual segmentation of vessel boundaries before visualization. This automated volumetric strategy for visualization and quantification of WSS may facilitate its clinical translation.
Keywords: 4D Flow MRI; cardiovascular; computational; segmentation-free; wall shear stress.
© 2018 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Cunningham KS, Gotlieb AI. The role of shear stress in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Lab Invest. 2005;85:9–23. - PubMed
-
- Macura KJ, Corl FM, Fishman EK, Bluemke DA. Pathogenesis in Acute Aortic Syndromes: Aortic Dissection, Intramural Hematoma, and Penetrating Atherosclerotic Aortic Ulcer. Am J Roentgenol. 2003;181(2):309–316. - PubMed
-
- Cecchi E, Giglioli C, Valente S, Lazzeri C, Gensini GF, Abbate R, Mannini L. Role of hemodynamic shear stress in cardiovascular disease. Athersclerosis. 2011;214:249–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials