Secretory microRNA-29 expression in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement
- PMID: 29518149
- PMCID: PMC5843286
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194238
Secretory microRNA-29 expression in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement
Abstract
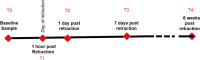
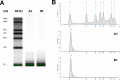
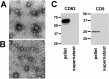
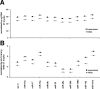
Secretory microRNAs (miRNAs) have been used increasingly as biomarkers for cancers, autoimmune diseases and inflammatory diseases. They are reported as being freely circulated or encapsulated in microvesicles such as exosomes. This study was performed to elucidate the presence of miRNAs with exosomes in human gingival crevicular fluid (GCF), and the expression profile of miRNA-29 during orthodontic tooth movement. Four healthy volunteer and fifteen orthodontic patients were enrolled in the study. Secretory miRNA in GCF was collected and analyzed using a bioanalyzer, realtime PCR and Western blot analysis. The expression profile of secretory miR-29 family in GCF was analyzed during the course of canine retraction for 6 weeks. The results demonstrated the presence of miRNAs in the GCF. After series of ultracentrifugation and RT-PCR array, exosome-depleted fractions and pellets were isolated and we found that secretory miRNAs were detected in both the exosome-associated fraction and the exosome-depleted supernatant fraction; however, the concentration of miRNAs was higher in the exosome-associated fraction than in the exosome-depleted fraction suggesting a close association between the secretory miRNAs and exosomes in GCF. We also demonstrated the increased expression profiles of miR-29 family during six weeks of orthodontic tooth movement in humans. Secretory miRNAs are present in GCF and secretory miRNA-29 family expression profiles increase during the tooth movement in humans. Secretory miRNA-29 in GCF could serve as potential biomarkers for periodontal remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ebert MS, Sharp PA. Roles for microRNAs in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell. 2012;149(3):515–524. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.005 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lehmann U. MicroRNA-profiling in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;667:113–125. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-811-9_8 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu A, Xu X. MicroRNA isolation from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;724:259–267. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-055-3_16 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gallo A, Tandon M, Alevizos I, Illei GG. The Majority of MicroRNAs Detectable in Serum and Saliva Is Concentrated in Exosomes. PloS one. 2012;7(3),:e30679 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030679 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY, Huang KH, Lee MJ, et al. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem. 2010;56(11):1733–1741. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

