Tannic Acid Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 29518944
- PMCID: PMC5876643
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10030068
Tannic Acid Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
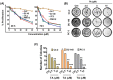
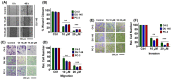
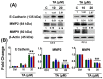
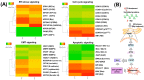
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an intriguing target with significant clinical importance in chemotherapy. Interference with ER functions can lead to the accumulation of unfolded proteins, as detected by transmembrane sensors that instigate the unfolded protein response (UPR). Therefore, controlling induced UPR via ER stress with natural compounds could be a novel therapeutic strategy for the management of prostate cancer. Tannic acid (a naturally occurring polyphenol) was used to examine the ER stress mediated UPR pathway in prostate cancer cells. Tannic acid treatment inhibited the growth, clonogenic, invasive, and migratory potential of prostate cancer cells. Tannic acid demonstrated activation of ER stress response (Protein kinase R-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) and inositol requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1)) and altered its regulatory proteins (ATF4, Bip, and PDI) expression. Tannic acid treatment affirmed upregulation of apoptosis-associated markers (Bak, Bim, cleaved caspase 3, and cleaved PARP), while downregulation of pro-survival proteins (Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL). Tannic acid exhibited elevated G₁ population, due to increase in p18INK4C and p21WAF1/CIP1 expression, while cyclin D1 expression was inhibited. Reduction of MMP2 and MMP9, and reinstated E-cadherin signifies the anti-metastatic potential of this compound. Altogether, these results demonstrate that tannic acid can promote apoptosis via the ER stress mediated UPR pathway, indicating a potential candidate for cancer treatment.
Keywords: ER stress; apoptosis; molecularly targeted therapeutics; tannic acid; unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Triggering of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Tannic Acid Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of Colorectal Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Aug 1;24(8):2705-2711. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.8.2705. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37642057 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of Unfolded Protein Response by Tannic Acid Triggers Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Jun 1;24(6):2029-2035. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.6.2029. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37378933 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by the anti-cancer agent, di-2-pyridylketone 4,4-dimethyl-3-thiosemicarbazone (Dp44mT): Activation of PERK/eIF2α, IRE1α, ATF6 and calmodulin kinase.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 1;109:27-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27059255
-
Dual role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Unfolded Protein Response Signaling Pathway in Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 5;20(18):4354. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184354. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31491919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ER Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Leukemia: Friend, Foe, or Both?Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 30;11(2):199. doi: 10.3390/biom11020199. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33573353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic efficacy of a novel βIII/βIV-tubulin inhibitor (VERU-111) in pancreatic cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 23;38(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-1009-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30674344 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity and cytotoxic and epigenetic effects of tannic acid-loaded chitosan nanoparticles.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 6;14(1):30405. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80771-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39638815 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Linked Polyphenol-Based Drug Nano-Self-Assemblies Engineered to Blockade Prostate Cancer Senescence.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Oct 23;11(42):38537-38554. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b14738. Epub 2019 Oct 8. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 31553876 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of Proline in Cell Behavior.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 12;9:728576. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.728576. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34458276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gambogic acid potentiates gemcitabine induced anticancer activity in non-small cell lung cancer.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 5;888:173486. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173486. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32805254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohapatro S.K., Dandapat M.C., Padhi N.C. Toxicity and side-effects of combination chemohormonal therapy of advanced breast cancer. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1992;90:39–42. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

