Key Players of Cisplatin Resistance: Towards a Systems Pharmacology Approach
- PMID: 29518977
- PMCID: PMC5877628
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19030767
Key Players of Cisplatin Resistance: Towards a Systems Pharmacology Approach
Abstract
The major obstacle in the clinical use of the antitumor drug cisplatin is inherent and acquired resistance. Typically, cisplatin resistance is not restricted to a single mechanism demanding for a systems pharmacology approach to understand a whole cell's reaction to the drug. In this study, the cellular transcriptome of untreated and cisplatin-treated A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells and their cisplatin-resistant sub-line A549rCDDP2000 was screened with a whole genome array for relevant gene candidates. By combining statistical methods with available gene annotations and without a previously defined hypothesis HRas, MAPK14 (p38), CCL2, DOK1 and PTK2B were identified as genes possibly relevant for cisplatin resistance. These and related genes were further validated on transcriptome (qRT-PCR) and proteome (Western blot) level to select candidates contributing to resistance. HRas, p38, CCL2, DOK1, PTK2B and JNK3 were integrated into a model of resistance-associated signalling alterations describing differential gene and protein expression between cisplatin-sensitive and -resistant cells in reaction to cisplatin exposure.
Keywords: CCL2; DOK1; HRas; JNK3; PTK2B; cellular signalling; cisplatin resistance; p38.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
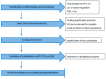
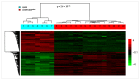
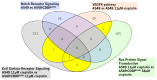
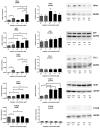
 ) and A549rCDDP2000 (
) and A549rCDDP2000 ( ) before (ctrl) and after treatment with 11 µM cisplatin (11) or 34 µM cisplatin (34) presented as mean ± SEM; as well as representative Western blots. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.01.
) before (ctrl) and after treatment with 11 µM cisplatin (11) or 34 µM cisplatin (34) presented as mean ± SEM; as well as representative Western blots. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.01.
 ) and A549rCDDP2000 (
) and A549rCDDP2000 ( ) after treatment with 11 µM cisplatin (11) or 34 µM cisplatin (34) expressed as mean ± SEM, as well as representative Western blots.* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.01.
) after treatment with 11 µM cisplatin (11) or 34 µM cisplatin (34) expressed as mean ± SEM, as well as representative Western blots.* p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.01.
References
-
- Besse B., Adjei A., Baas P., Meldgaard P., Nicolson M., Paz-Ares L., Reck M., Smit E.F., Syrigos K., Stahel R., et al. 2nd ESMO Consensus Conference on Lung Cancer: Non-small-cell lung cancer first-line/second and further lines of treatment in advanced disease. Ann. Oncol. 2014;25:1475–1484. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu123. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

