Oxidative DNA Damage and Carotid Intima Media Thickness as Predictors of Cardiovascular Disease in Prediabetic Subjects
- PMID: 29518984
- PMCID: PMC5872363
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd5010015
Oxidative DNA Damage and Carotid Intima Media Thickness as Predictors of Cardiovascular Disease in Prediabetic Subjects
Abstract
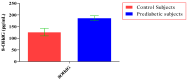
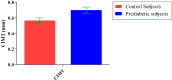
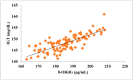
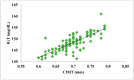
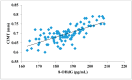
Prediabetes is considered as a risk factor for the development of diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. The present study was conducted with the aim of finding out the relationship between oxidative DNA damage and carotid intima media thickness for the prediction of cardiovascular disease in prediabetic subjects. The study included 100 prediabetic subjects and 100 normal individuals as controls. In both cases and controls, 8-OHdG was measured by ELISA, and CIMT was measured by B mode ultrasonography. Both 8-OHdG and CIMT were significantly higher in subjects with prediabetes as compared to controls (185.80 ± 10.72 pg/mL vs. 126.13 ± 16.01 pg/mL, p < 0.001 and 0.70 ± 0.04 mm vs. 0.57 ± 0.03 mm, p < 0.001, respectively). There was significant and positive correlation of IGT with 8-OHdG (r = 0.783; p < 0.001) and CIMT (r = 0.787; p < 0.001) in prediabetic subjects. Moreover, 8-OHdG showed significant positive correlation with CIMT (r = 0.704; p < 0.001) in prediabetic subjects. In conclusion, increased 8-OHdG and CIMT in prediabetic subjects indicate that biochemical changes of atherosclerosis start even before the onset of diabetes mellitus. Hence, 8-OHdG and CIMT could be used as indicators of cardiovascular disease risk in these subjects.
Keywords: 8-hydroxy-2-deoxy-guanosine; cardiovascular disease; carotid intima media thickness; prediabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship between Atherogenic Indices and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Prediabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study from Central India.Med Sci (Basel). 2018 Jul 5;6(3):55. doi: 10.3390/medsci6030055. Med Sci (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29976917 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis by Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Epicardial Adipose Tissue Thickness in Prediabetes.Angiology. 2016 Nov;67(10):961-969. doi: 10.1177/0003319716643669. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Angiology. 2016. PMID: 27069111
-
Oxidative DNA damage correlates with carotid artery atherosclerosis in hemodialysis patients.Hemodial Int. 2011 Oct;15(4):453-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-4758.2011.00568.x. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Hemodial Int. 2011. PMID: 22111813 Clinical Trial.
-
Carotid intima-media thickness: an index for subclinical atherosclerosis in type 1 diabetes.J Trop Pediatr. 2006 Feb;52(1):39-45. doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmi071. Epub 2005 Jul 6. J Trop Pediatr. 2006. PMID: 16000343
-
CIMT does not identify early vascular changes in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia survivors.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020 Feb;29(2):243-249. doi: 10.17219/acem/115082. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32073764
Cited by
-
Trends in Guideline-Driven Revascularization in Diabetic Patients with Multivessel Coronary Heart Disease.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019 Nov 18;6(4):41. doi: 10.3390/jcdd6040041. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2019. PMID: 31752091 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of the Mediterranean Diet on Healthy Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 24;24(5):4491. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054491. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between Atherogenic Indices and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Prediabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study from Central India.Med Sci (Basel). 2018 Jul 5;6(3):55. doi: 10.3390/medsci6030055. Med Sci (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29976917 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of Human Intervention Studies Evaluating the Impact of the Mediterranean Diet on Markers of DNA Damage.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 13;11(2):391. doi: 10.3390/nu11020391. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30781873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Significance of Elevated Xanthine Dehydrogenase Levels and Hyperuricemia in Patients with Sepsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 8;24(18):13857. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813857. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hackworth N., Moore S.N., Hardie E., Critchley C., Buzwell S., Crafti N., Kyrios M. A Risk Factor Profile for Pre-diabetes: Biochemical, Behavioural, Psychosocial and Cultural Factors. J. Appl. Psychol. 2007;3:14–26. doi: 10.7790/ejap.v3i2.89. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

