Biosynthesis of Rishirilide B
- PMID: 29518990
- PMCID: PMC5872131
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics7010020
Biosynthesis of Rishirilide B
Abstract
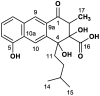
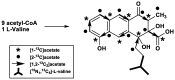
Rishirilide B was isolated from Streptomyces rishiriensis and Streptomyces bottropensis on the basis of its inhibitory activity towards alpha-2-macroglobulin. The biosynthesis of rishirilide B was investigated by feeding experiments with different 13C labelled precursors using the heterologous host Streptomyces albus J1074::cos4 containing a cosmid encoding of the gene cluster responsible for rishirilide B production. NMR spectroscopic analysis of labelled compounds demonstrate that the tricyclic backbone of rishirilide B is a polyketide synthesized from nine acetate units. One of the acetate units is decarboxylated to give a methyl group. The origin of the starter unit was determined to be isobutyrate.
Keywords: biosynthesis; polyketides; rishirilide; streptomyces.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Iwaki H., Nakayama Y., Takahashi M., Uetsuki S., Kido M. Structures of rishirilides A and B, α2-macroglobulin inhibitors produced by Streptomyces rishiriensis OFR-1056. J. Antibiot. 1984;XXXVII:9–11. - PubMed
-
- Moore B.S., Hertweck C. Biosynthesis and attachment of novel bacterial polyketide synthase starter units. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002;19:70–99. - PubMed
-
- Ubukata M., Cheng X.C., Uzawa J., Isono K. Biosynthesis of the dialkylmaleic anhydride-containing antibiotics, tautomycin and tautomycetin. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1. 1995:2399–2404. doi: 10.1039/p19950002399. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

