Modeling human diseases with induced pluripotent stem cells: from 2D to 3D and beyond
- PMID: 29519889
- PMCID: PMC5868991
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.156166
Modeling human diseases with induced pluripotent stem cells: from 2D to 3D and beyond
Abstract
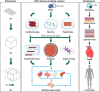
The advent of human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) presents unprecedented opportunities to model human diseases. Differentiated cells derived from iPSCs in two-dimensional (2D) monolayers have proven to be a relatively simple tool for exploring disease pathogenesis and underlying mechanisms. In this Spotlight article, we discuss the progress and limitations of the current 2D iPSC disease-modeling platform, as well as recent advancements in the development of human iPSC models that mimic in vivo tissues and organs at the three-dimensional (3D) level. Recent bioengineering approaches have begun to combine different 3D organoid types into a single '4D multi-organ system'. We summarize the advantages of this approach and speculate on the future role of 4D multi-organ systems in human disease modeling.
Keywords: Disease modeling; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Organ-on-chip; Organoid.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Assawachananont J., Mandai M., Okamoto S., Yamada C., Eiraku M., Yonemura S., Sasai Y. and Takahashi M. (2014). Transplantation of embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived 3D retinal sheets into retinal degenerative mice. Stem Cell Rep. 2, 662-674. 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.03.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baxter M., Withey S., Harrison S., Segeritz C.-P., Zhang F., Atkinson-Dell R., Rowe C., Gerrard D. T., Sison-Young R., Jenkins R. et al. (2015). Phenotypic and functional analyses show stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells better mimic fetal rather than adult hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 62, 581-589. 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

