Analysis of chronic aortic regurgitation by 2D and 3D echocardiography and cardiac MRI
- PMID: 29519957
- PMCID: PMC5881430
- DOI: 10.1530/ERP-17-0083
Analysis of chronic aortic regurgitation by 2D and 3D echocardiography and cardiac MRI
Abstract
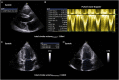
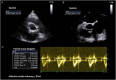
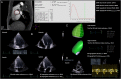
Purpose The study compares the feasibility of the quantitative volumetric and semi-quantitative approach for quantification of chronic aortic regurgitation (AR) using different imaging modalities. Methods Left ventricular (LV) volumes, regurgitant volumes (RVol) and regurgitant fractions (RF) were assessed retrospectively by 2D, 3D echocardiography and cMRI in 55 chronic AR patients. Semi-quantitative parameters were assessed by 2D echocardiography. Results 22 (40%) patients had mild, 25 (46%) moderate and 8 (14%) severe AR. The quantitative volumetric approach was feasible using 2D, 3D echocardiography and cMRI, whereas the feasibility of semi-quantitative parameters varied considerably. LV volume (LVEDV, LVESV, SVtot) analyses showed good correlations between the different imaging modalities, although significantly increased LV volumes were assessed by cMRI. RVol was significantly different between 2D/3D echocardiography and 2D echocardiography/cMRI but was not significantly different between 3D echocardiography/cMRI. RF was not statistically different between 2D echocardiography/cMRI and 3D echocardiography/cMRI showing poor correlations (r < 0.5) between the different imaging modalities. For AR grading by RF, moderate agreement was observed between 2D/3D echocardiography and 2D echocardiography/cMRI and good agreement was observed between 3D echocardiography/cMRI. Conclusion Semi-quantitative parameters are difficult to determine by 2D echocardiography in clinical routine. The quantitative volumetric RF assessment seems to be feasible and can be discussed as an alternative approach in chronic AR. However, RVol and RF did not correlate well between the different imaging modalities. The best agreement for grading of AR severity by RF was observed between 3D echocardiography and cMRI. LV volumes can be verified by different approaches and different imaging modalities.
Keywords: 2D echocardiography; 3D echocardiography; Doppler echocardiography; aortic regurgitation; cardiac MRI.
Figures

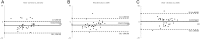
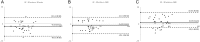
Similar articles
-
Quantitative Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation Secondary to Mitral Valve Prolapse by Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Echocardiography.Am J Cardiol. 2015 Nov 1;116(9):1405-10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.07.064. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Am J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 26372213
-
Comparison of two- and three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography to cardiac magnetic resonance imaging for assessment of paravalvular regurgitation after transcatheter aortic valve implantation.Am J Cardiol. 2014 Jun 1;113(11):1859-66. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.02.038. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Am J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24837265
-
Accuracy of three-dimensional versus two-dimensional echocardiography for quantification of aortic regurgitation and validation by three-dimensional three-directional velocity-encoded magnetic resonance imaging.Am J Cardiol. 2013 Aug 15;112(4):560-6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.04.025. Epub 2013 May 15. Am J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23683972
-
European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging/Cardiovascular Imaging Department of the Brazilian Society of Cardiology recommendations for the use of cardiac imaging to assess and follow patients after heart transplantation.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Sep;16(9):919-48. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev139. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26139361 Review.
-
Meta-Analysis of Transthoracic Echocardiography Versus Cardiac Magnetic Resonance for the Assessment of Aortic Regurgitation After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation.Am J Cardiol. 2019 Oct 15;124(8):1246-1251. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.07.036. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31466694 Review.
Cited by
-
Valid and Reproducible Quantitative Assessment of Cardiac Volumes by Echocardiography in Patients with Valvular Heart Diseases-Possible or Wishful Thinking?Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 6;13(7):1359. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13071359. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046577 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy and reliability of novel semi-automated two-dimensional layer specific speckle tracking software for quantifying left ventricular volumes and function.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 30;14(8):e0221204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221204. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31469858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lancellotti P, Tribouilloy C, Hagendorff A, Moura L, Popescu BA, Agricola E, Monin JL, Pierard LA, Badano L, Zamorano JL. European Association of Echocardiography – recommendations for the assessment of valvular regurgitation. Part 1: aortic and pulmonary regurgitation (native valve disease). European Journal of Echocardiography 2010. 11 223–244. (10.1093/ejechocard/jeq030) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lancellotti P, Tribouilloy C, Hagendorff A, Popescu BA, Edvardsen T, Pierard LA, Badano L, Zamorano JL. Recommendations for the echocardiographic assessment of native valvular regurgitation: an executive summary from the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging. European Heart Journal: Cardiovascular Imaging 2013. 14 611–644. (10.1093/ehjci/jet105) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhogbi WA, Adams D, Bonow RO, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Hahn RT, Han Y, Hung J, Lang RM, et al Recommendations for noninvasive evaluation of native valvular regurgitation – a report from the American Society of Echocardiography Developed in Collaboration with the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography 2017. 30 303–371. (10.1016/j.echo.2017.01.007) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

