Modulating the water channel AQP4 alters miRNA expression, astrocyte connectivity and water diffusion in the rodent brain
- PMID: 29520011
- PMCID: PMC5843607
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-22268-y
Modulating the water channel AQP4 alters miRNA expression, astrocyte connectivity and water diffusion in the rodent brain
Abstract
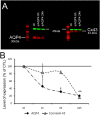
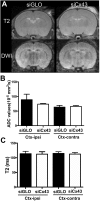
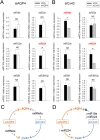
Aquaporins (AQPs) facilitate water diffusion through the plasma membrane. Brain aquaporin-4 (AQP4) is present in astrocytes and has critical roles in normal and disease physiology. We previously showed that a 24.9% decrease in AQP4 expression after in vivo silencing resulted in a 45.8% decrease in tissue water mobility as interpreted from magnetic resonance imaging apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC). Similar to previous in vitro studies we show decreased expression of the gap junction protein connexin 43 (Cx43) in vivo after intracortical injection of siAQP4 in the rat. Moreover, siAQP4 induced a loss of dye-coupling between astrocytes in vitro, further demonstrating its effect on gap junctions. In contrast, silencing of Cx43 did not alter the level of AQP4 or water mobility (ADC) in the brain. We hypothesized that siAQP4 has off-target effects on Cx43 expression via modification of miRNA expression. The decreased expression of Cx43 in siAQP4-treated animals was associated with up-regulation of miR224, which is known to target AQP4 and Cx43 expression. This could be one potential molecular mechanism responsible for the effect of siAQP4 on Cx43 expression, and the resultant decrease in astrocyte connectivity and dramatic effects on ADC values and water mobility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Targeted deletion of Aqp4 promotes the formation of astrocytic gap junctions.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Dec;222(9):3959-3972. doi: 10.1007/s00429-017-1448-5. Epub 2017 May 27. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 28551776
-
New possible roles for aquaporin-4 in astrocytes: cell cytoskeleton and functional relationship with connexin43.FASEB J. 2005 Oct;19(12):1674-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-3281fje. Epub 2005 Aug 15. FASEB J. 2005. PMID: 16103109
-
Brain water mobility decreases after astrocytic aquaporin-4 inhibition using RNA interference.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011 Mar;31(3):819-31. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.163. Epub 2010 Sep 29. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2011. PMID: 20877385 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin-4 in Astroglial Cells in the CNS and Supporting Cells of Sensory Organs-A Comparative Perspective.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 26;17(9):1411. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091411. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27571065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of aquaporin 4 in the brain.Vet Clin Pathol. 2012 Mar;41(1):32-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-165X.2011.00390.x. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Vet Clin Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22250904 Review.
Cited by
-
Microphysiological Systems for Neurodegenerative Diseases in Central Nervous System.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Sep 16;11(9):855. doi: 10.3390/mi11090855. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32947879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Interference RNA Targeting Connexin-43 Improves Motor Function and Limits Astrogliosis After Juvenile Traumatic Brain Injury.ASN Neuro. 2019 Jan-Dec;11:1759091419847090. doi: 10.1177/1759091419847090. ASN Neuro. 2019. PMID: 31194577 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Cx43 and AQP4 Proteins, and the Capture of 3 kDa Dextran in Subpial Astrocytes of the Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex after Both Sham Surgery and Sciatic Nerve Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 12;25(20):10989. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010989. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456773 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of microRNAs in Aquaporin Regulation.Front Chem. 2018 Jun 21;6:238. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00238. eCollection 2018. Front Chem. 2018. PMID: 29977890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AQP4 is an Emerging Regulator of Pathological Pain: A Narrative Review.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Nov;43(8):3997-4005. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01422-9. Epub 2023 Oct 21. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37864629 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

