Pharmacokinetics, distribution and anti-tumor efficacy of liposomal mitoxantrone modified with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptor-specific peptide
- PMID: 29520138
- PMCID: PMC5833774
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S150512
Pharmacokinetics, distribution and anti-tumor efficacy of liposomal mitoxantrone modified with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptor-specific peptide
Abstract
Background: A previous study developed a novel luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) receptor-targeted liposome. The aim of this study was to further assess the pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and anti-tumor efficacy of LHRH receptor-targeted liposomes loaded with the anticancer drug mitoxantrone (MTO).
Methods: Plasma and tissue distribution profiles of LHRH receptor-targeted MTO-loaded liposomes (LHRH-MTO-LIPs) were quantified in healthy mice or a xenograft tumor nude mouse model of MCF-7 breast cancer, and were compared with non-targeted liposomes and a free-drug solution.
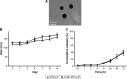
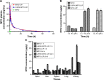
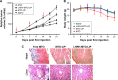
Results: The LHRH-MTO-LIPs demonstrated a superior pharmacokinetic profile relative to free MTO. The first target site of accumulation is the kidney, followed by the liver, and then the tumor; maximal tumor accumulation occurs at 4 h post-administration. Moreover, the LHRH-MTO-LIPs exhibited enhanced inhibition of MCF-7 breast cancer cell growth in vivo compared with non-targeted MTO-loaded liposomes (MTO-LIPs) and free MTO.
Conclusion: The novel LHRH receptor-targeted liposome may become a viable platform for the future targeted treatment of cancer.
Keywords: gonadorelin; liposome; luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptor; mitoxantrone; tumor targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Graham SM, Carlisle R, Choi JJ, et al. Inertial cavitation to non-invasively trigger and monitor intratumoral release of drug from intravenously delivered liposomes. J Control Release. 2014;178:101–107. - PubMed
-
- Pérez-Herrero E, Fernández-Medarde A. Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;93:52–79. - PubMed
-
- Zununi Vahed S, Salehi R, Davaran S, Sharifi S. Liposome-based drug co-delivery systems in cancer cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;71:1327–1341. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

