Design and synthesis of nanoscaled IQCA-TAVV as a delivery system capable of antiplatelet activation, targeting arterial thrombus and releasing IQCA
- PMID: 29520141
- PMCID: PMC5833776
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S150205
Design and synthesis of nanoscaled IQCA-TAVV as a delivery system capable of antiplatelet activation, targeting arterial thrombus and releasing IQCA
Abstract
Background: Arterial thrombosis has been associated with a series of pathological conditions, and the discovery of arterial thrombosis inhibitor is of clinical importance.
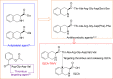
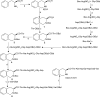
Methods: By analyzing the pharmacophores of anti-platelet agents, thrombus targeting peptide and anti-thrombotic nano-systems 3S-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquino-line-3-carbonyl-Thr-Ala-Arg-Gly-Asp(Val)-Val (IQCA-TAVV) was designed and prepared as a nano-scaled arterial thrombosis inhibitor.
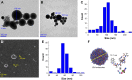
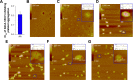
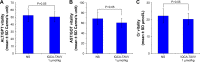
Results: In vitro the nanoparticles of IQCA-TAVV were able to adhere onto the surface of activated platelets, attenuate activated platelets to extend pseudopodia and inhibit activated platelets to form aggregators. In vivo IQCA-TAVV targeted arterial thrombus, dose dependently inhibited arterial thrombosis with a 1 nmol/kg of minimal effective dose, and the activity waŝ1670 folds of that of aspirin.
Conclusion: IQCA-TAVV represented the design, preparation and application of nanomedicine capable of adhering on the surface of activated platelets, attenuating platelet activation, targeting arterial thrombus and inhibiting arterial thrombosis.
Keywords: antithrombosis; arterial thrombosis; nanodelivery; thrombus targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures







References
-
- Agnello L, Bivona G, Lo Sasso B, et al. Galectin-3 in acute coronary syndrome. Clin Biochem. 2017;50(13–14):797–803. - PubMed
-
- Asrar ul Haq M, Erickson M, Rankin J, Whelan A. Late strut fracture within a partially resorbed bioresorbable vascular scaffold: a possible cause of late scaffold thrombosis and acute coronary syndrome. Heart Lung Circ. 2017;26(4):e26–e28. - PubMed
-
- Laine M, Frere C, Cuisset T, et al. Potential mechanism of acute stent thrombosis with bivalirudin following percutaneous coronary intervention in acute coronary syndromes. Int J Cardiol. 2016;220:496–500. - PubMed
-
- deVeber GA, Kirton A, Booth FA, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of arterial ischemic stroke in children: the Canadian pediatric ischemic stroke registry. Pediatr Neurol. 2017;69:58–70. - PubMed
-
- Arnaez J, Garcia-Alix A. Extracerebral thrombosis in symptomatic neonatal arterial ischemic stroke. Eur J Pediatr Neurol. 2017;21(4):687–688. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

