Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for control of microbial biofilms: a review
- PMID: 29520143
- PMCID: PMC5834171
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S146195
Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for control of microbial biofilms: a review
Abstract
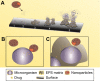
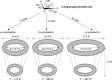
Since the dawn of civilization, it has been understood that pathogenic microorganisms cause infectious conditions in humans, which at times, may prove fatal. Among the different virulent properties of microorganisms is their ability to form biofilms, which has been directly related to the development of chronic infections with increased disease severity. A problem in the elimination of such complex structures (biofilms) is resistance to the drugs that are currently used in clinical practice, and therefore, it becomes imperative to search for new compounds that have anti-biofilm activity. In this context, nanotechnology provides secure platforms for targeted delivery of drugs to treat numerous microbial infections that are caused by biofilms. Among the many applications of such nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems is their ability to enhance the bioactive potential of therapeutic agents. The present study reports the use of important nanoparticles, such as liposomes, microemulsions, cyclodextrins, solid lipid nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, and metallic nanoparticles, in controlling microbial biofilms by targeted drug delivery. Such utilization of these nanosystems has led to a better understanding of their applications and their role in combating biofilms.
Keywords: anti-biofilm activity; microbial biofilms; nanotechnology systems.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P. Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13(1):34–40. - PubMed
-
- Aparna MS, Yadav S. Biofilms: microbes and disease. Braz J Infect Dis. 2008;12(6):526–530. - PubMed
-
- Bjarnsholt T. The role of bacterial biofilms in chronic infections. APMIS. 2013;121(136):1–58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

