Kanglaite reverses multidrug resistance of HCC by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 29520149
- PMCID: PMC5833758
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S153814
Kanglaite reverses multidrug resistance of HCC by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via PI3K/AKT pathway
Retraction in
-
Kanglaite Reverses Multidrug Resistance of HCC by Inducing Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest via PI3K/AKT Pathway [Retraction].Onco Targets Ther. 2024 Feb 13;17:99-100. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S463641. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38371878 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Multidrug resistance (MDR) frequently contributes to the failure of chemotherapeutic treatments in patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Revealing the molecular mechanism of MDR is indispensable for the development of effective chemotherapeutic drugs.
Purpose: Due to the low-toxicity modulators to inhibit MDR, we considered that Kanglaite (KLT) is a potential agent for reversing MDR in HCC.
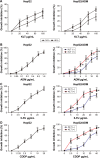
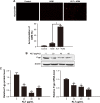
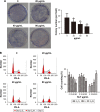
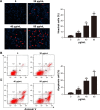
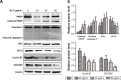
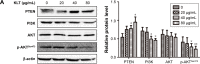
Materials and methods: BEL-7402/5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and HepG2/adriamycin (ADM) were analyzed for cell viability, colony formation assay, cell scratch assay, and cell cycle analysis and apoptosis assay by flow cytometry. The expression of PARP, caspase-3, Bax, Bcl-2, CDC25C, Cyclin B1 and phosphorylation of PTEN, PI3K, and AKT in HepG2/ADM cells were detected by western blotting.
Results: The proliferation of drug-resistant cell lines BEL-7402/5-FU and HepG2/ADM pretreated with KLT was significantly inhibited when compared with drug alone. KLT could increase the accumulation of ADM in HepG2/ADM cells. In this study, we found that KLT treatment notably reduced cell viability, induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human HepG2/ADM and BEL-7402/5-FU cells, and effectively reversed the MDR by p-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibition. Moreover, KLT decreased the phosphorylation of AKT and PI3K in KLT-treated HepG2/ADM cells. These data together implied that KLT might reverse drug resistance in HCC by blocking the PI3K/AKT signaling.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that KLT reversed MDR of human HCC by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT pathway; apoptosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; kanglaite; multidrug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Lotz C, Kelleher DK, Gassner B, Gekle M, Vaupel P, Thews O. Role of the tumor microenvironment in the activity and expression of the p-glycoprotein in human colon carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2007;17(1):239–244. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

